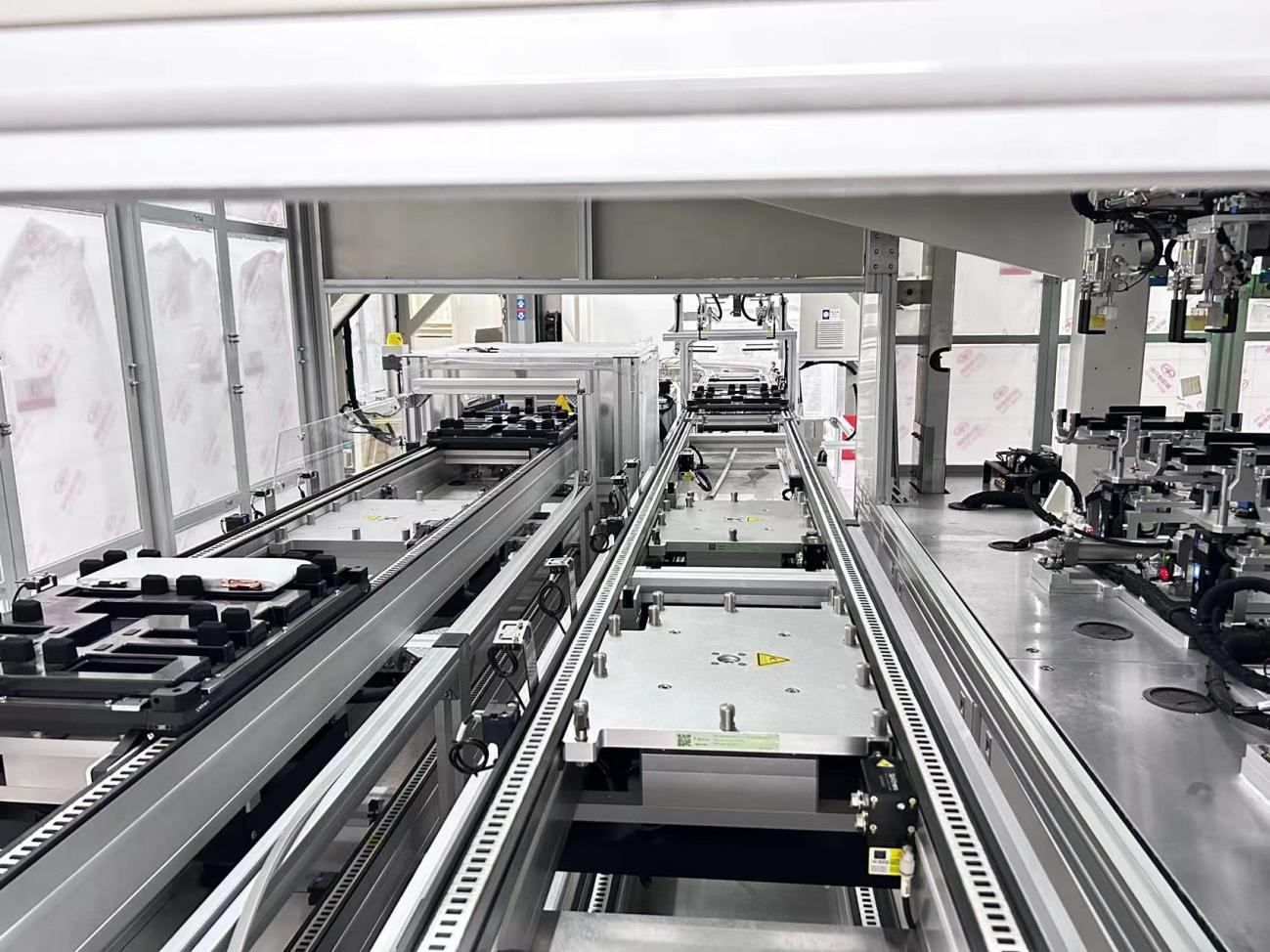
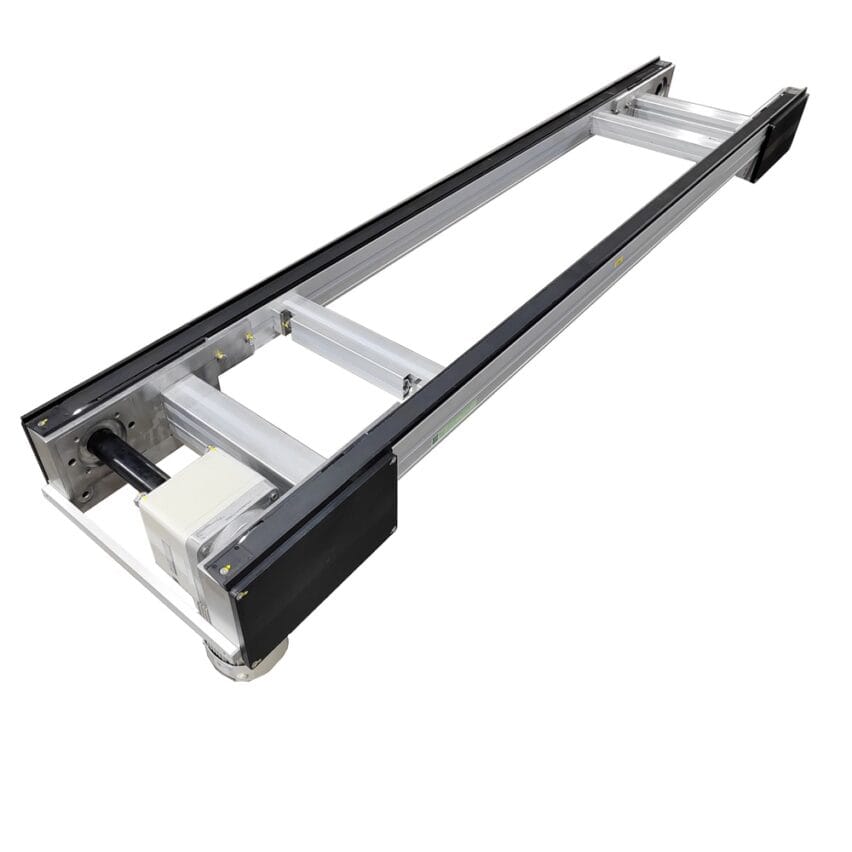
in areas such as modern logistics and manufacturing production.Pallet conveying systemsplays a vital role. However, in the course of its operation, some common problems may arise:
For example, a production line is running at full speed when suddenly there's a ”click” - a pallet is stuck. Have you ever been caught off guard by such an unexpected situation? Don't worry, today we will dismantle the secrets behind these problems, and at the same time find a solution, so you can easily deal with a variety of unexpected situations.

I. Pallet-related failures
| defective phenomenon | Possible causes | cure |
| Pallet jam | 1. Deformation, damage to pallets 2. Dirt/foreign matter on rails 3. Guide wheel deflection 4. Pallet oversize | 1. Replacement of damaged pallets 2. Clean rails and remove foreign objects 3. Adjustment of guide wheel position 4. Check pallet specifications and replace with conforming items |
| Pallet Offset / Derailment | 1. Loose guides 2. Uneven chain/belt tension 3. Wear on bottom of pallets | 1. Fastening of guides 2. Adjustmentsdrive systemstrain 3. Replacement of trays or repair of bottoms |
| Pallet stacking/collision | 1. Sensor misdetection (pallet position) 2. Improper speed regulation 3. Blocker failure | 1. Cleaning/calibrating photoelectric sensors 2. Adjustment of conveying speed 3. Repair of blocking cylinders or solenoid valves |

II. Failure of conveyor components
| defective phenomenon | Possible causes | cure |
| Chain/belt slippage | 1. Insufficient tensioning 2. Driving wheel wear 3. Decreased friction due to oil contamination | 1. Adjustment of the tensioning device 2. Replacement of drive wheels 3. Clean oil and improve sealing |
| Chain breakage / detachment | 1. Excessive wear and tear 2. Over-tensioning 3. Foreign object stuck in | 1. Replacement of chains 2. Adjustment of proper tension 3. Cleaning of foreign objects, protective coverings |
| The drum is stuck and won't turn | 1. Bearing damage 2. Dust/foreign body intrusion 3. Lubrication failure | 1. Replacement of bearings 2. Clean and dust cover 3. Regular grease replenishment |
| Conveyor belt deflection | 1. The rollers are not mounted parallel to each other 2. Roller tilt 3. Material offloading | 1. Calibration of drum leveling 2. Adjusting the angle of the rollers 3. Optimization of material placement |
III. Drive system failures
| defective phenomenon | Possible causes | cure |
| Motor overheating/rattling | 1. Excessive load (mechanical jamming) 2. Voltage instability 3. Bearing damage | 1. Removal of mechanical resistance 2. Inspection of power lines 3. Replacement of motor bearings |
| Reducer oil leakage/vibration | 1. Deterioration of seals 2. Gear wear 3. Loose mounting base | 1. Replacement of seals 2. Inspection of gear sets 3. Fastening of floor bolts |
| Inverter alarm shutdown | 1. Overload protection 2. Incorrect parameterization 3. Poor heat dissipation | 1. Check load after reset 2. Recalibration of parameters 3. Clean the cooling fan dust |

IV. Sensor and control failures
| defective phenomenon | Possible causes | cure |
| Photoelectric sensor false trigger | 1. Lens contamination 2. External light interference 3. Sensitivity set too high | 1. Cleaning the sensor window 2. Hooding or shielding of interference sources 3. Adjustment of sensitivity |
| No output signal from PLC | 1. Procedural errors 2. Damaged I/O module 3. Communication breakdown | 1. Inspection/reloading procedures 2. Replacement of I/O modules 3. Checking network connectivity |
| Emergency stop button not working | 1. Line breaks 2. Contact oxidation 3. PLC input point failure | 1. Checking line breaks 2. Sanding contacts or replacing buttons 3. Replacement of PLC input points |

V. Other frequently asked questions
| defective phenomenon | Possible causes | cure |
| abnormal noise | 1. Lack of oil in bearings 2. Chain wear slack 3. Loose structural elements | 1. Supplementary lubrication 2. Tension or replace the chain 3. Fastening of bolts |
| Frequent system starts and stops | 1. Power supply voltage fluctuations 2. Overload protection trigger 3. Poor heat dissipation | 1. Adding voltage regulators 2. Reducing loads or upgrading equipment 3. Improvement of ventilation |
| Insufficient lubrication leads to wear | 1. Lack of regular maintenance 2. Clogged oil lines 3. Wrong type of lubricant | 1. Establishment of a regular maintenance schedule 2. Cleaning of oil lines 3. Replacement of the correct lubricant |

Six,Systematic maintenance recommendations:
①Daily inspections: Clean rails/sensors, listen for noises, check tray status.
②Weekly Maintenance: Replenish lubrication points, check chain/belt tension, tighten bolts.
③quarterly maintenance: Full cleaning, replacement of worn parts (bearings, seals), calibration of sensors.
④Annual overhaul: Motor/reducer teardowns, control system upgrades, corrosion protection of structural components.
Key Tips:
60%'sPallet conveying lineFailure stems from insufficient lubrication and dust contamination. It is recommended to increase the level of protection in dusty environments and adopt automatic lubrication system to reduce human negligence. For inverter, PLC and other precision equipment, need to maintain the ambient temperature ≤ 40 ℃ and humidity ≤ 80%.
Conveyor line reliability and longevity can be dramatically improved by categorizing and managing trouble spots and strictly enforcing preventive maintenance.