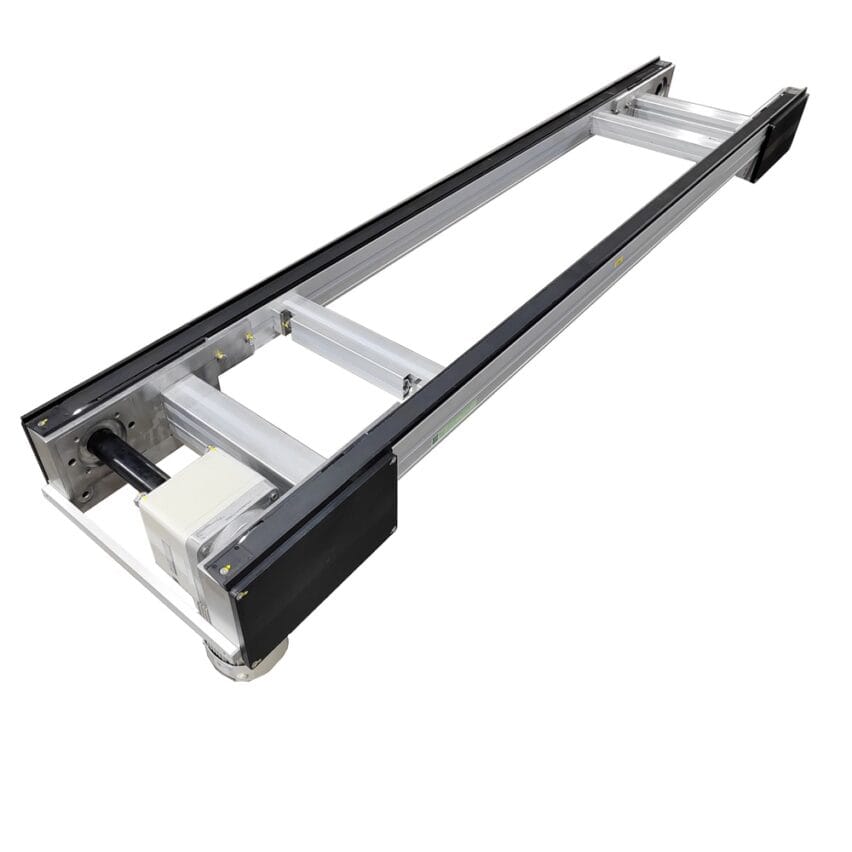
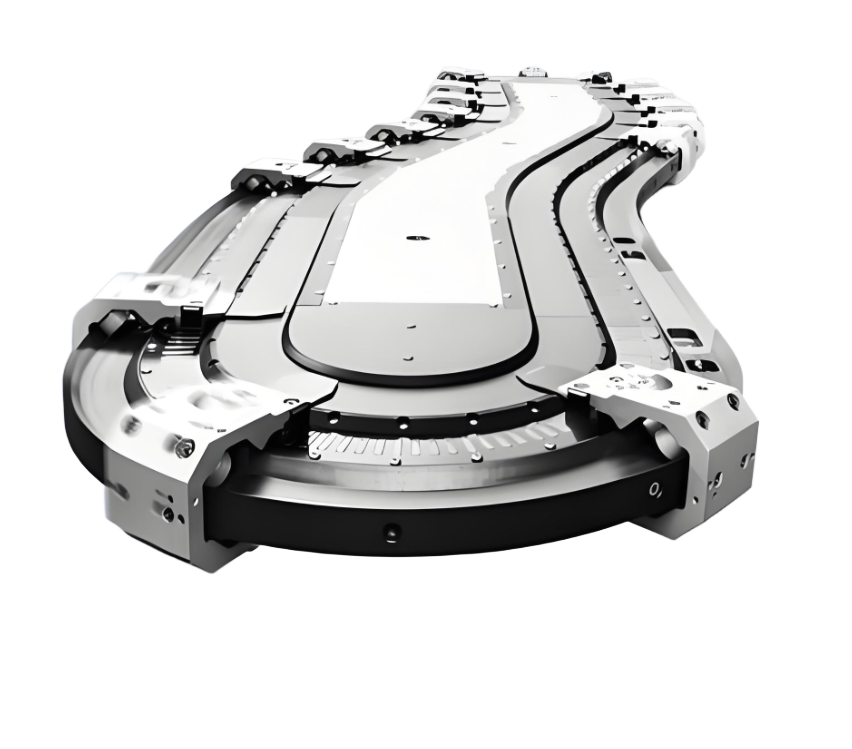
I. Differential Principle: The Physical Code of Mechanical Speed Increase
The core mystery of the multiplier chain isDesign of diameter difference between roller and roller. When the chain is running at speed ν, the actual speed of the work plate can be up to the chain's2.5 to 3 times, whose physical formula is:
Vtooling board
= ν × (1 + R/r)
(R: roller radius, r: roller radius). For example, if R/r=1.5, the speed of the work plate is 2.5 ν. Suchmechanical leveraged incremental speedNo additional energy consumption is required, but efficiency can be significantly increased over long distances, especially for continuous assembly scenarios such as electronics and automotive.
Industry Paradox BreakthroughWhen the magnetic levitation technology is hotly contested, a home appliance giant has invested 200 million in the transformation of the speed chain system, completed four production line restructuring in three years, the introduction of new models to reduce the cost of 60%. This confirms -In highly variable market environments, reconfigurability of mechanical systems is more strategically valuable than absolute speed.
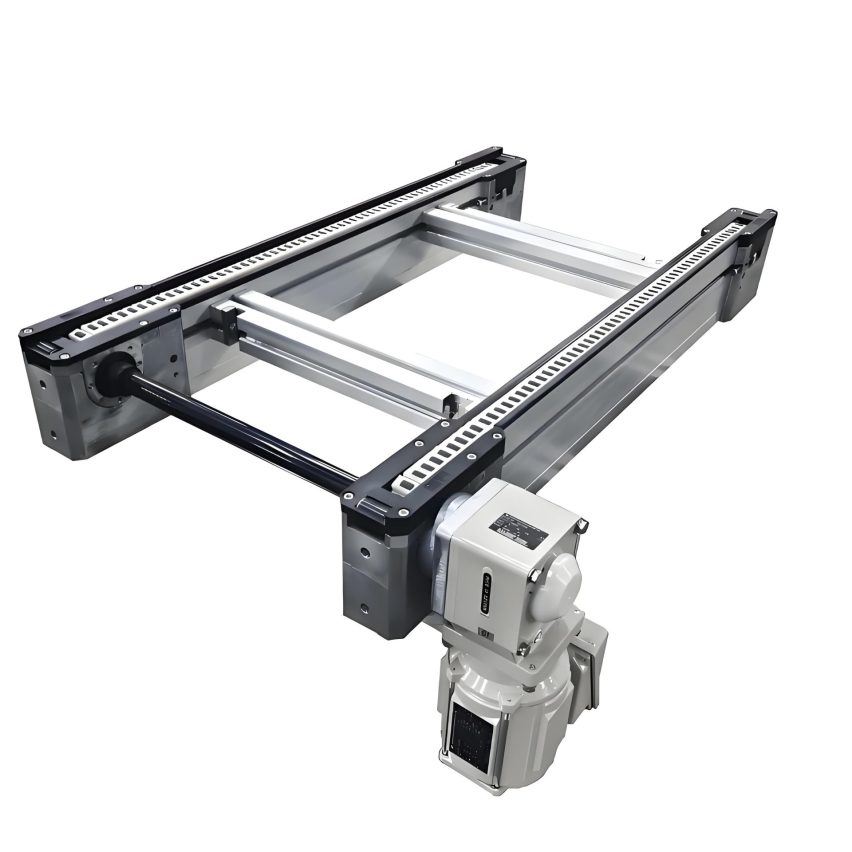
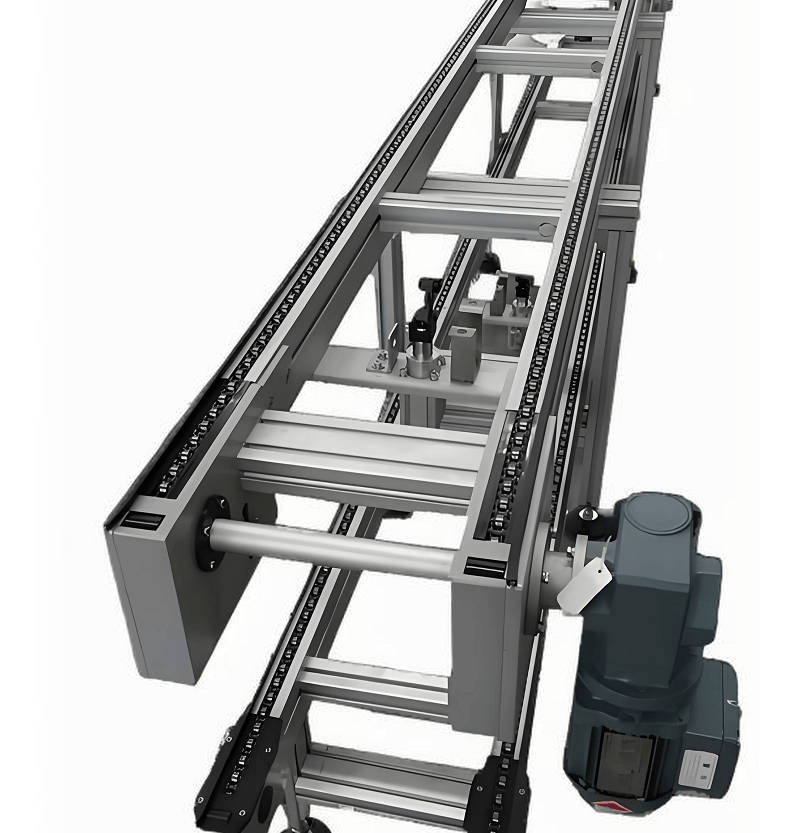
II. Anatomy of a structure: seven modules working together
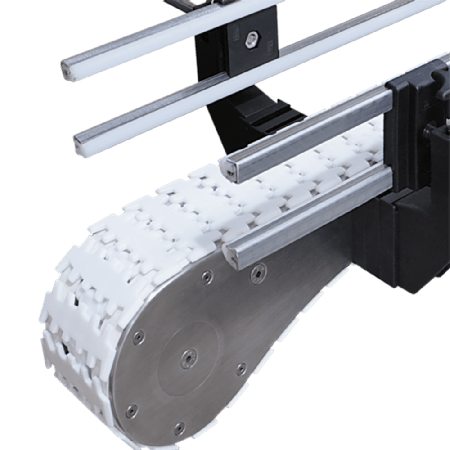
1. Chain system: balance of precision and durability
| typology | octave ratio | Applicable Scenarios | innovative design |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering Plastic Chain | 2.5 times | 3C electronic assembly | Anti-static coating to avoid circuit breakdown |
| Steel Roller Chain | 3 times | Automotive Engine Transport | High temperature resistant coating (120°C) |
| Double Pitch Accumulator Chain | 2.5-3 times | mixed flow production | Localised line stoppages do not affect overall operation |
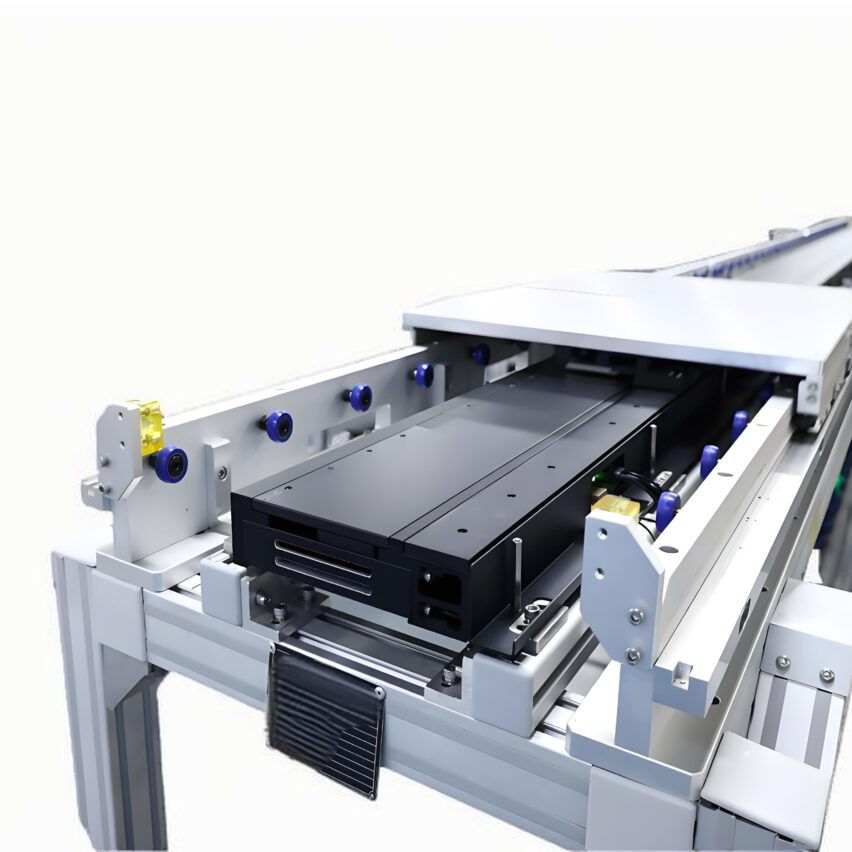
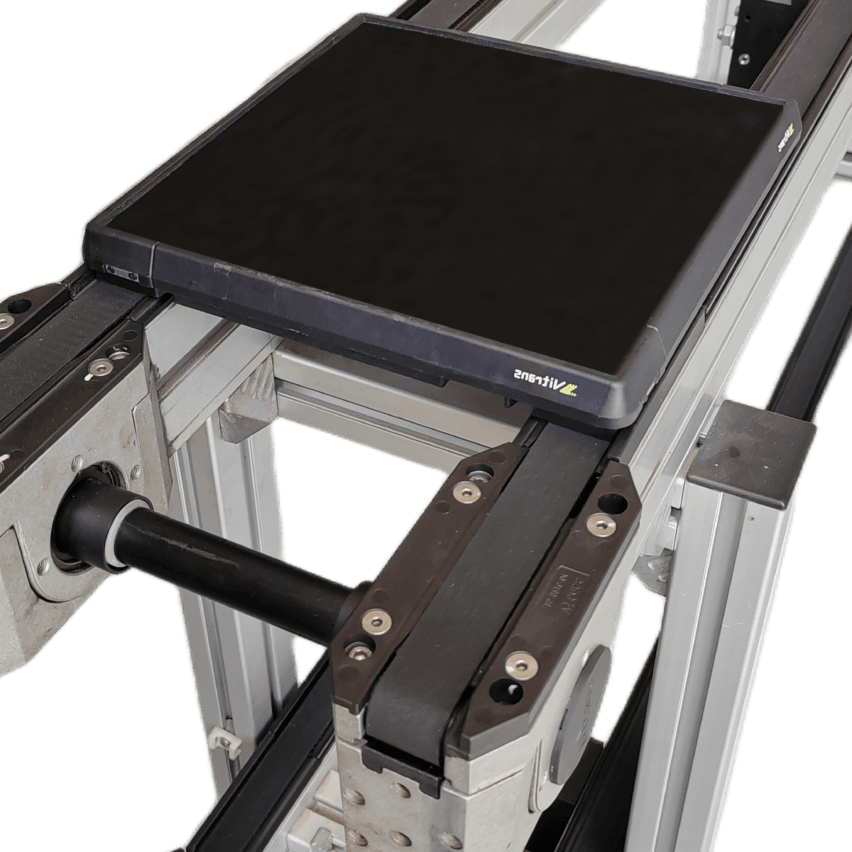
2. Intelligent evolution of workplace panels
- Gradient material structure: Surface layer of 0.5mm silicon carbide coating to enhance wear resistance, core layer filled with aluminium honeycomb (density 0.28g/cm³), load-bearing nodes reinforced with titanium alloy (180MPa compressive)
- Dynamic power supply systemsCopper alloy electrode + graphene contact layer (resistance 0.5Ω), 3 times longer life than traditional carbon brushes, better stability under strong electromagnetic environment.
- data-termination: RFID inlays store process parameters, compressing automotive mixing line changeover time from 4 hours to 45 minutes.
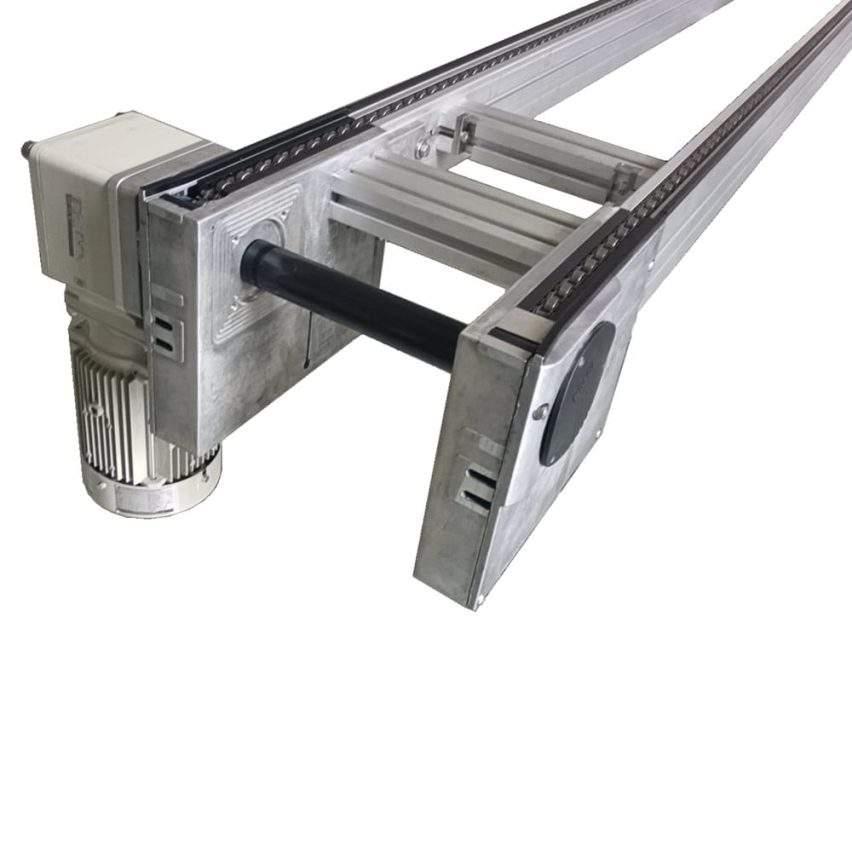
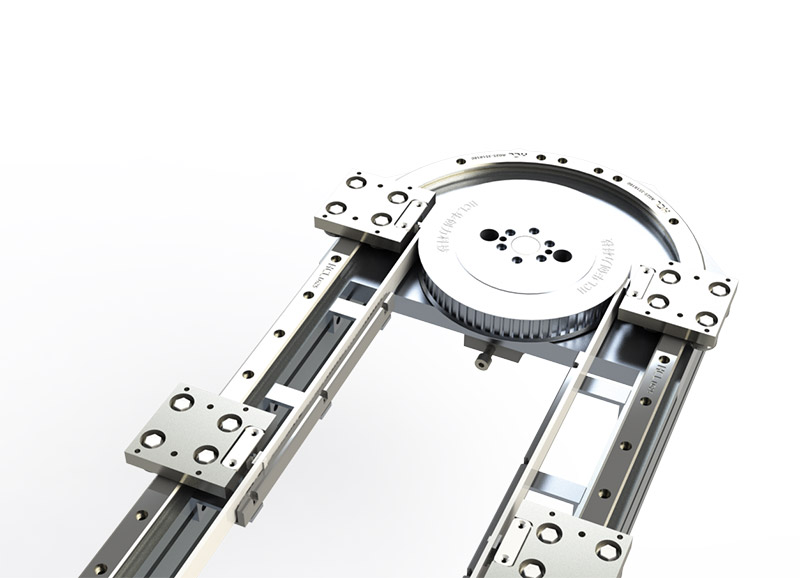
3. Drive and control centre
- Double sprocket synchronised drive: Centre distance error ≤0.5mm, avoiding the risk of jumping chain
- Three speed control modes: Low-speed start (0.3m/s), normal operation (1.0m/s), high-speed return (1.5m/s), S-type acceleration and deceleration curves to reduce the impact of the
- blockchain traceability: Record each stop position deviation, train AI compensation model, cumulative accuracy improvement of 40%
III. Production line design: the four-step rule from demand to landing
▎ First step: precise definition of parameters
- load capacity: Steel chain + hydraulic vibration absorber for light loads (200kg)
- environmental adaptation: High-temperature scenarios with optional 120°C resistant coating, 304 stainless steel plate for food and pharmaceutical lines (colony residue <5CFU/cm²)
- spatial arrangement: Single-section drive ≤ 40m (anti-chain sagging), small factories recommend 10-15m line body + 3-6 stations
▎ Step 2: Modular Selection Strategy
- drive system: Gear motor under 2.2kW (small and medium loads), with heavy hammer type tensioning device (droop ≤ 2% pitch)
- safety protection: Emergency stop button every 5 metres (response 0.2 seconds), sheet metal shield (opening ≤ 12mm)
- Extended InterfaceReservation of jacking and panning positions, support for AGV connection (logistics efficiency of a factory increased by 50%)
▎ Step 3: Digital twin previews
The case of Tesla's Shanghai factory:
- Virtual production line simulates multiplier chain docking with AGVs to reduce collision risk by 90%
- Energy model optimisation leads to annual power savings of 120,000 kWh on a single line
▎ Step 4: Intelligent Maintenance System
- Predictive maintenance: laser rangefinder to monitor chain sag, current sensors to pre-determine rail wear
- Lubricating AI Decision MakingDynamically adjust the oiling cycle according to temperature, humidity and load (high temperature chain oil every 500 hours).
IV. Application Scenarios: Three Battlegrounds for the Efficiency Revolution
▶ Consumer Electronics Field
Dongguan mobile phone factory adopts triple speed chain after:
- Assembly beat compressed from 120 seconds/unit to 78 seconds
- Workpiece accumulation function reduces staging area by 40%
- Antistatic Design Yield Improvement 2.3%
▶ Automotive Manufacturing Innovation
- Engine assembly: double sprocket drive to carry 500kg cylinder block, synchronous accuracy ±0.5mm.
- New energy battery: 1.5 tonne pack braking distance reduced to 15cm (±1mm positioning)
▶ Upgrading of food and medicine
- Lubrication-free design: food-grade engineering plastics bearings eliminate risk of contamination
- Cold chain adaptability: stable modulus of elasticity in -20°C environment ensures smooth conveying.
V. Future battlegrounds: 2026 technology road map
1. Hybrid drive systems
- Speed chain + magnetic drive module with variable speed: 2m/s in regular zone → automatic speed reduction to 0.3m/s in assembly zone
- Phase change material guide: adaptive deformation compensation for thermal expansion and contraction, accuracy fluctuation <0.1mm
2. Energy self-recycling
- Piezoelectric ceramics capture vibration energy: powering workbench sensors and reducing wiring complexity
- Direct-drive PV technology: Xiangyang plant's 56 MW of PV meets 30% production line power consumption
3. Cognitive intelligence fusion
- Workpiece digital twin: real-time mapping of operating status and prognosis of mechanical failures
- AI dynamic scheduling: automatically adjust the workstation blocking strategy according to the order priority.
Self-questioning: a breakdown of the core issues
Q: Why is the Speed Chain Line better suited to trunk assembly lines than AGVs?
Answer.Essentially a game of precision and efficiency--
- Core Advantages::
- Continuous conveying speed >5m/s (AGV average 1.5m/s)
- ±0.05mm hard positioning (AGV relies on laser navigation ±5mm)
- Carrying capacity of up to 240kg per unit area (AGV pallets typically ≤100kg)
- collaborative scenarioA factory uses a jack-up pan conveyor to connect with AGVs, the heavy load section is conveyed at high speed by the chain, and the end section is flexibly sorted by AGVs.
Q: How can small plants be deployed at low cost?
Answer.Modular Subtractive Design::
- Streamline controls: Replacement of PLC with inverter (cost saving 40%)
- Lightweight construction:: 40 * 80mm aluminium profile frame (50% lighter than carbon steel)
- shared drive: Single motor driving twin parallel bodies
Q: How do you ensure stability in high dust environments?
Answer.Three defence technology combinations::
- Enclosed rails: Side sliding cover design to block dust intrusion
- Dry Lubrication System: Graphene Coating Replaces Lubricants
- Sprocket self-cleaning: Scraper unit removes dust from the rollers in real time.
The Ultimate Revelation: The essence of the multiplier chain assembly line isThe Philosophy of Rigid and Flexible Manufacturing--Rigid transmission of power, flexible adaptation to change. While Industry 4.0 is chasing the "unmanned factory", a company has embedded vibration sensors in the work plate, allowing workers to tap the equipment to emergency braking. This reminds us.The most advanced automation never replaces humans, but amplifies the value of their decisions.