Why is your production line always down due to broken pallets? You can lose $800,000 by overloading 3kg! In Industrial Automation.The wrong choice of load bearing for the doubler chain disc was the root cause of the 90%'s failure.As an automation engineer. As an automation engineer for 12 years, I have seen too many companies pay a terrible price for neglecting the details of load-bearing - from the electronics factory chain loss 3 times a month, to the machinery factory overload 10% crushed guideway production. This article will dismantle the whole process of load-bearing selection, to help you avoid these "invisible bombs".
Basic question: What is the multiplier chain workpiece disc load-bearing? Why does it determine life and death?
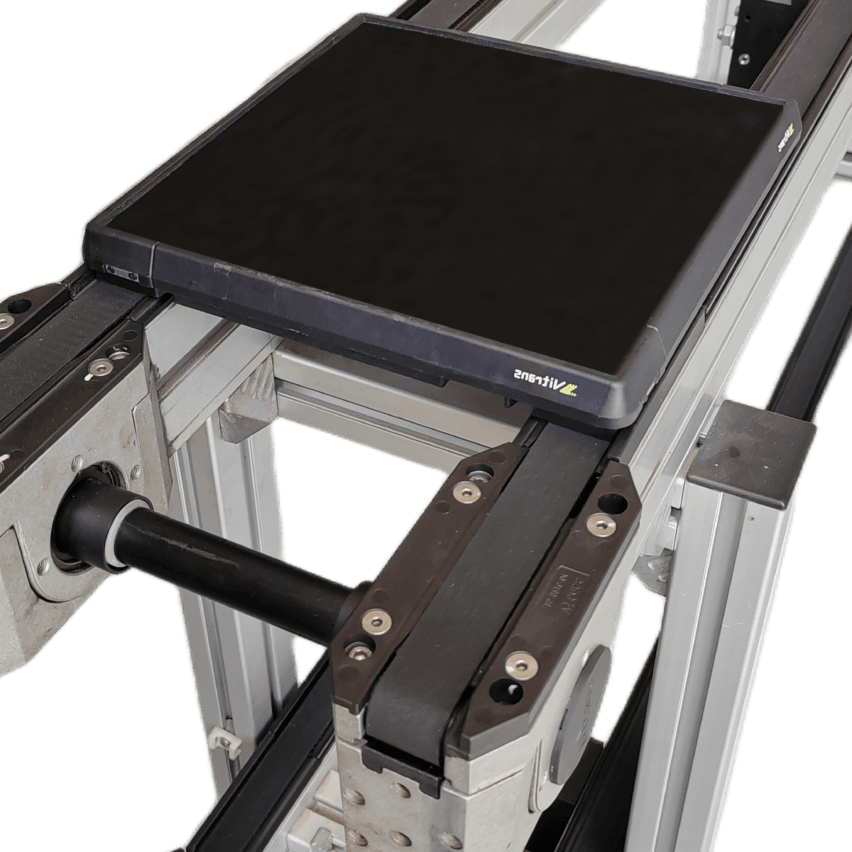
The nature of the load-bearing nature of the pallet is the dynamic load limit.The maximum weight that can be safely carried by a pallet in motion. It is by no means a static test value, but is affected by a combination of chain speed, friction and inertial impact. For example, a pallet with a static load of 80kg may see its actual load plummet to 50kg at 15m/min.
Why is load bearing so critical?Overloading directly triggered chain breakage, guide deformation and even full production stop. A hardware factory in Dongguan only because of overloading 3 kg, the loss of 800,000 maintenance fees; Zhejiang auto parts factory more overloading due to rush work, lost 20 million orders. The core of the chain is like a lorry, overloading must be "overturned" - light chain (single link load-bearing 5KG) strong plug 8KG metal parts, loss of 3 times a month; heavy-duty chain (50KG +) overloading 10%, 3 months crushed equipment.
How is the load-bearing range divided?Graded according to pallet size:
- Miniature pallet (160 x 160 mm): Upper limit 20KG, suitable for light load scenarios such as electronic components.
- Lightweight pallet (240 x 240mm): Upper limit 40KG, suitable for mobile phone parts assembly.
- Heavy duty pallet (400 x 400mm): Limit 80KG, specialising in heavy workpieces such as engines.
personal experienceMany factories mistakenly think that "the larger the size of the more insurance", the result is 480 × 640mm pallet weight of 12.85KG, anti-increase in chain tension 30% - the optimal solution is to match the workpiece of the smallest The optimal solution is the smallest pallet that matches the workpiece.
Scenario question: How to accurately calculate load bearing? Where to get the key parameters?
Step 1: Calculate the load density
Formula.Unit load (kg/cm) = (workpiece weight + pallet weight) / pallet support length
Example: 10kg workpiece + 2kg pallet on 320mm pallet → (12kg/32cm) = 0.375kg/cm.
It should be noted here: the weight of the pallet can be found in the table (e.g. 400 x 400mm aluminium alloy pallet weighs about 3.31KG).
Step 2: Match the limits of the conveying medium
- Plastic friction strip line: Unit load ≤1.0kg/cm → Select the AC2/H model.
- Steel Friction Bar Line: Unit load ≤2.0kg/cm → Select the AC2 model.
Key data sourcesManufacturers such as Wei Chuang provide actual measurement coefficient table - speed > 14m/min, the upper limit of the load should be × 1.6 speed factor (i.e. 80KG pallet actual load limit of 50KG).
Step 3: Accounting for dynamic margins
Dynamic load bearing ≠ static value! Must be calibrated with the formula:
Dynamic load = static load / (1 + 0.1 x speed value)
For example, static 80KG pallet at 15m/min speed: 80/(1+1.5)=32KG.
The coefficient of friction is the invisible killer: at speeds >10m/min, friction leads to load-bearing attenuation 8%-15% (see table):
| Type of friction | ratio | attenuation |
|---|---|---|
| Pallet vs. chain (fa) | 0.10 | 8%-12% |
| Chain vs. slide (fc) | 0.08 | 5%-10% |
Personal experience: Newcomers often ignore the impact of temperature - the environment > 80 ℃ when the strength of plastic pallets down 40%, be sure to switch to metal.
Solution: How can an overload disaster be avoided? What will save the production line?
If you don't choose the right load bearing? A chain of disasters erupts
- direct loss: Chain breakage, guide rail crushing, such as Guangdong Machinery Factory overload 10% operation, shutdown loss is enough to buy a suite.
- hidden costs: Motor overload damage (4 sets of drive systems replaced per year), energy consumption soaring 30%, repair costs exceeding the cost of purchasing the machine.
- safety risk: Emergency stop failures, personnel injuries, and a plant's actual load capacity plummeting by 40% due to modification of the spreader.
three-step problem solving method
- Load check: Real-time load monitoring with dynamic sensors, by which the Shandong enterprise avoided three chain breakage incidents.
- Safety Redundancy: Reserve 20% load-bearing space when selecting the type - Shenzhen electronic factory to use this to extend the life of the production line by 2 times.
Formula validation: Target load × 1.2 ≤ Nominal value of pallet. - Intelligent Early Warning: Adding overload emergency stop device (response <0.5 seconds), Wuhan Machinery Plant has achieved 0 major failures for the whole year.
Real-world case: 90KG robot line rebirth story
In a factory, a pallet was deformed due to a 90KG load:
- sore point: Exceeded the upper limit of plastic pallets (80KG), and the production line was jammed frequently.
- solution (a math problem)::
- Switching aluminium alloy tray (400 x 480mm with 12mm thick sides).
- Adding steel pipe reinforcement, the load capacity is raised to 110KG.
- Reduce speed to 8m/min to reduce shock.
- efficacy: Cost increase ¥200/pallet, downtime decrease 90%.
Exclusive data:: Industry Report 2025 shows thatReasonable selection to reduce the failure rate 67%In addition, the leading companies have adopted the standard of "0.1kg per centimetre of load-bearing capacity".
A final word of advice.Load-bearing is not a numbers game, but a battleground for the laws of physics - even the most expensive equipment will collapse if the dynamic factor is ignored. Those cases of "saving a little money and losing a lot" are essentially the arrogance of Newton.
: Overload cases and redundancy design for assembly lines
: Formula for selecting the speed chain and friction coefficient.
:: Structural strength and safety standards
: Relationship between material and load capacity
: Pallet size and weight parameters
: Load calculation and length matching
: Tension confirmation and velocity effects