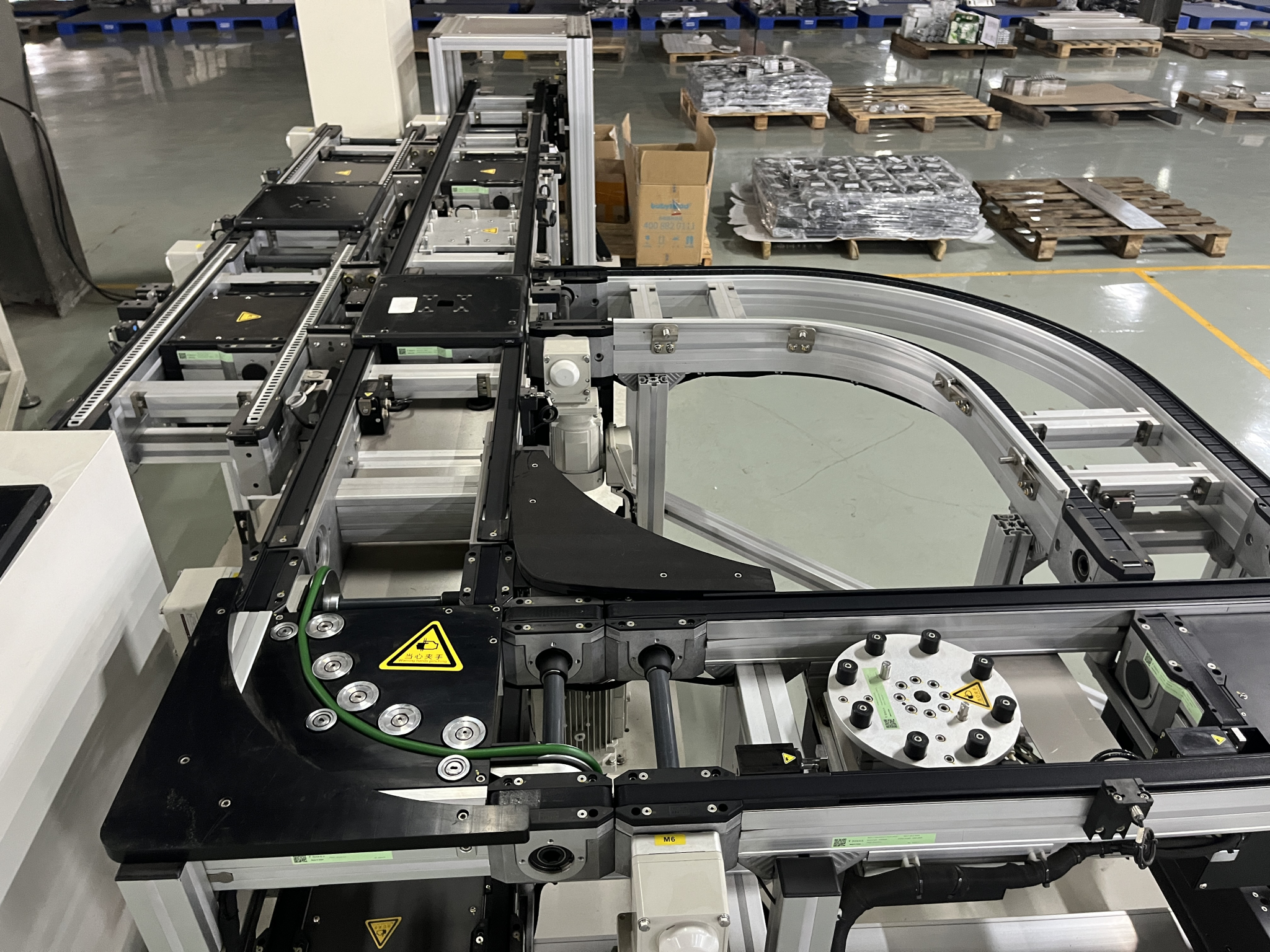
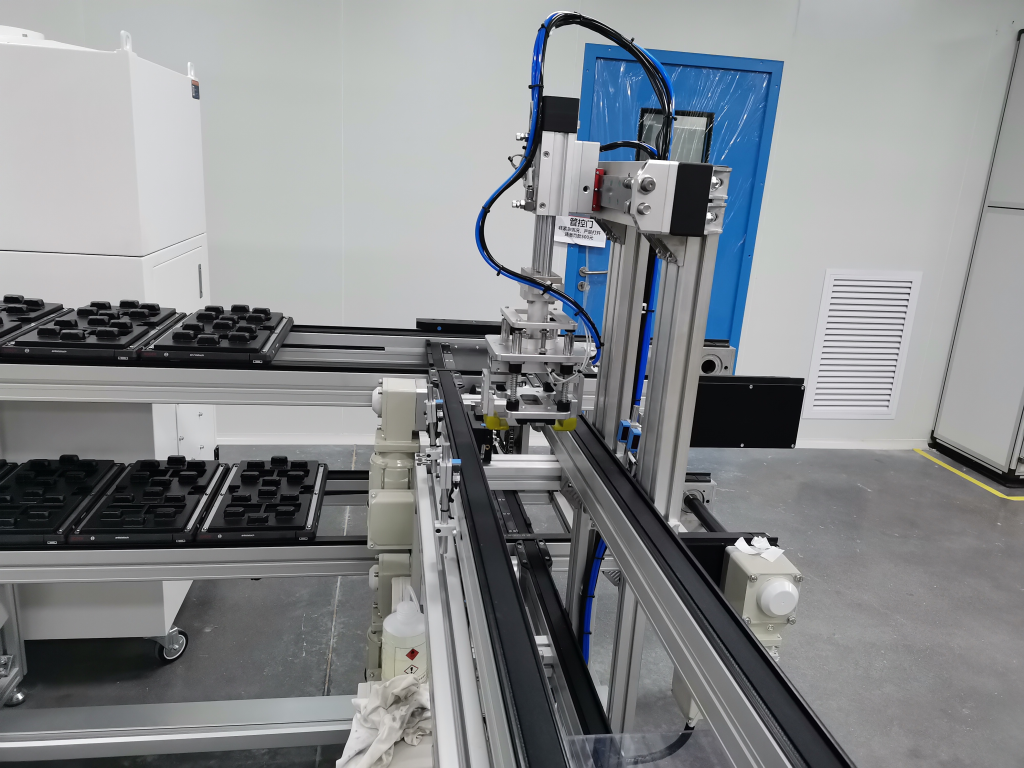
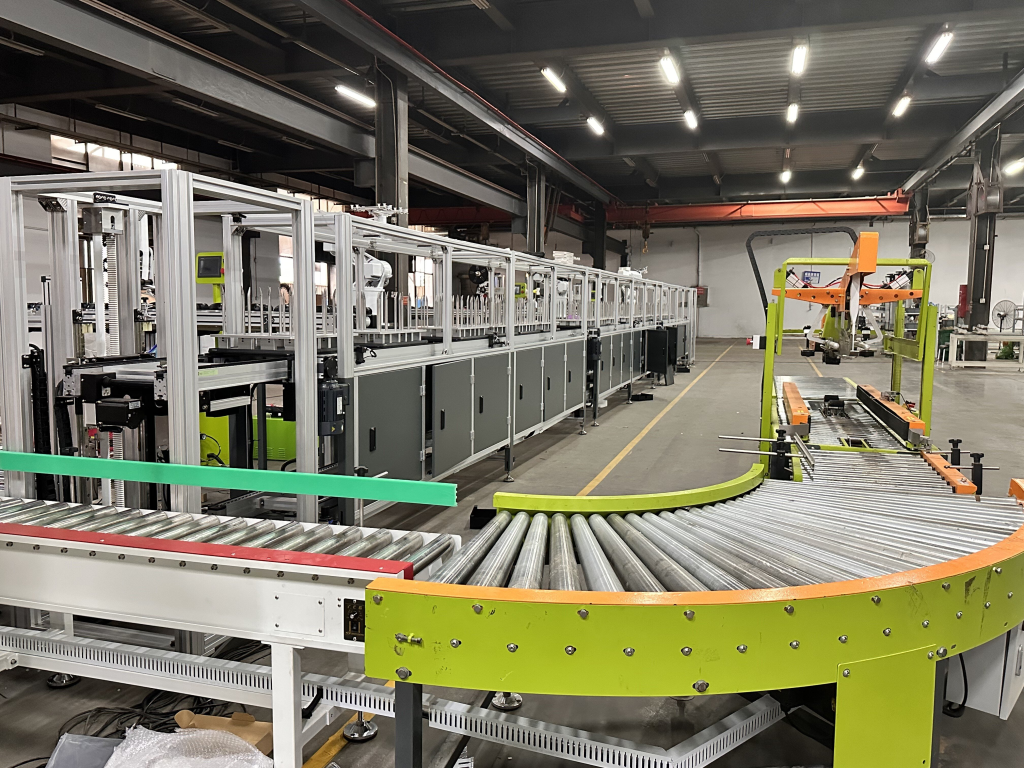
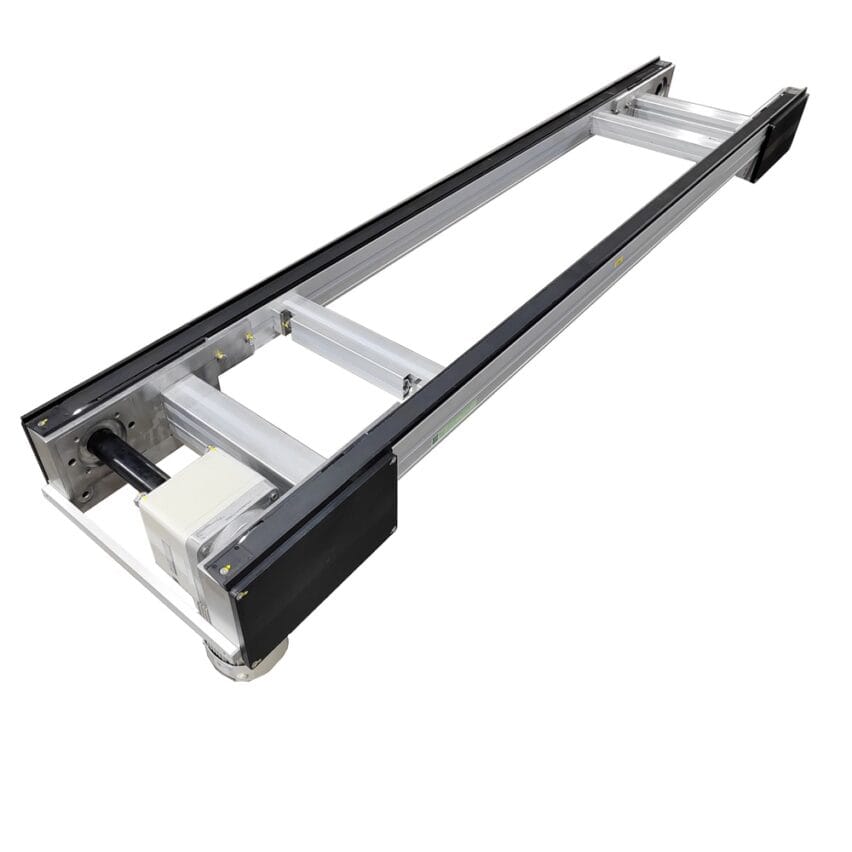
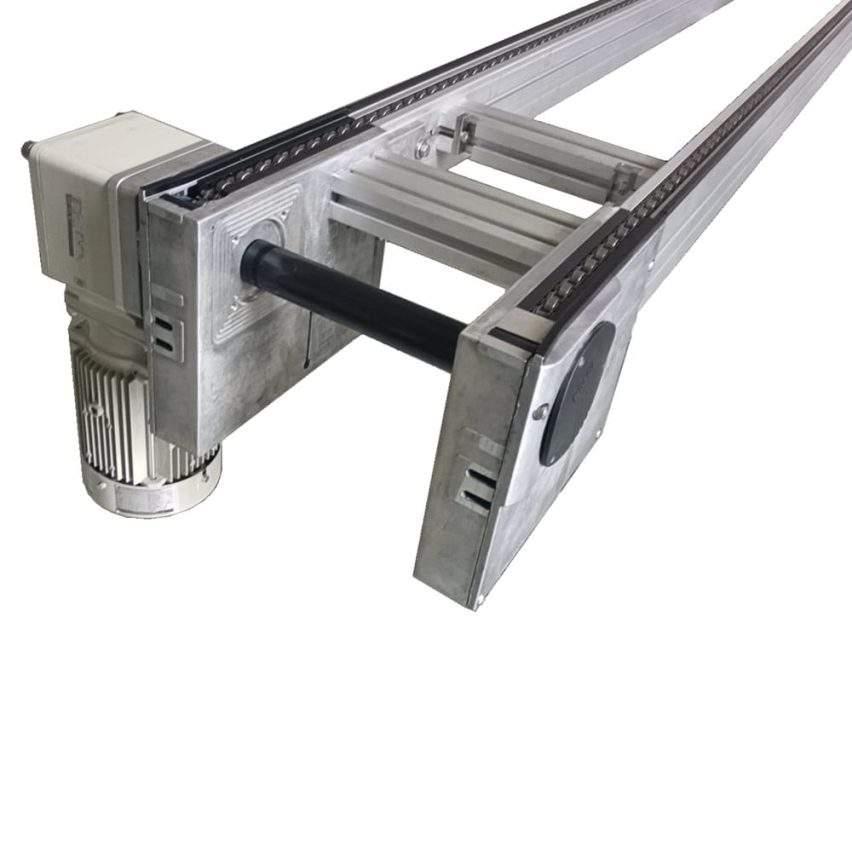
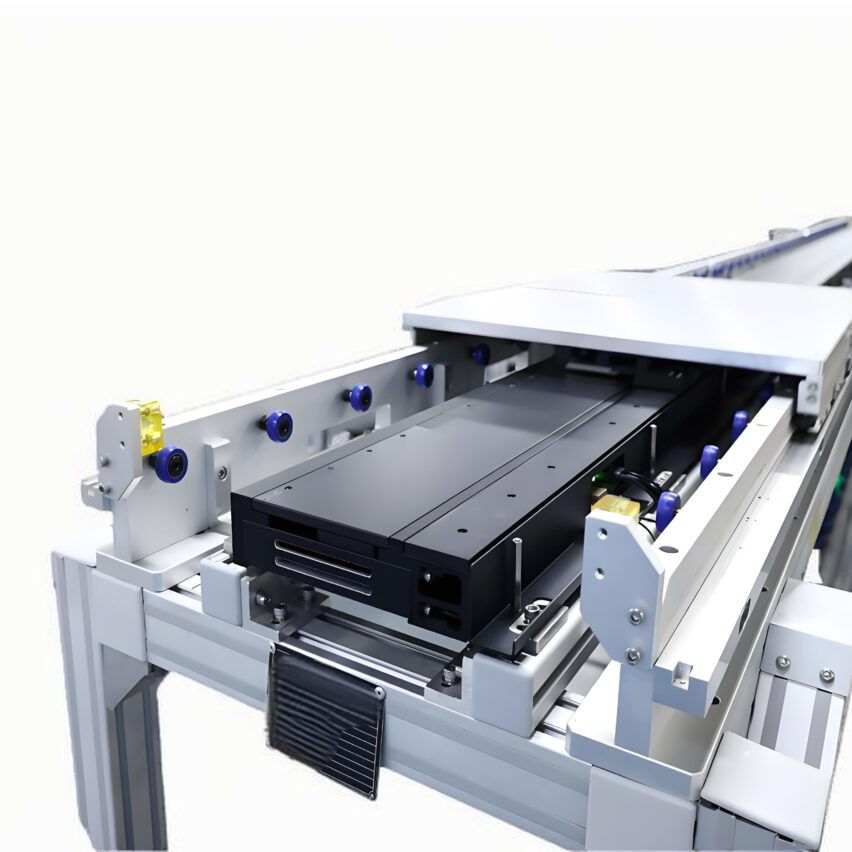
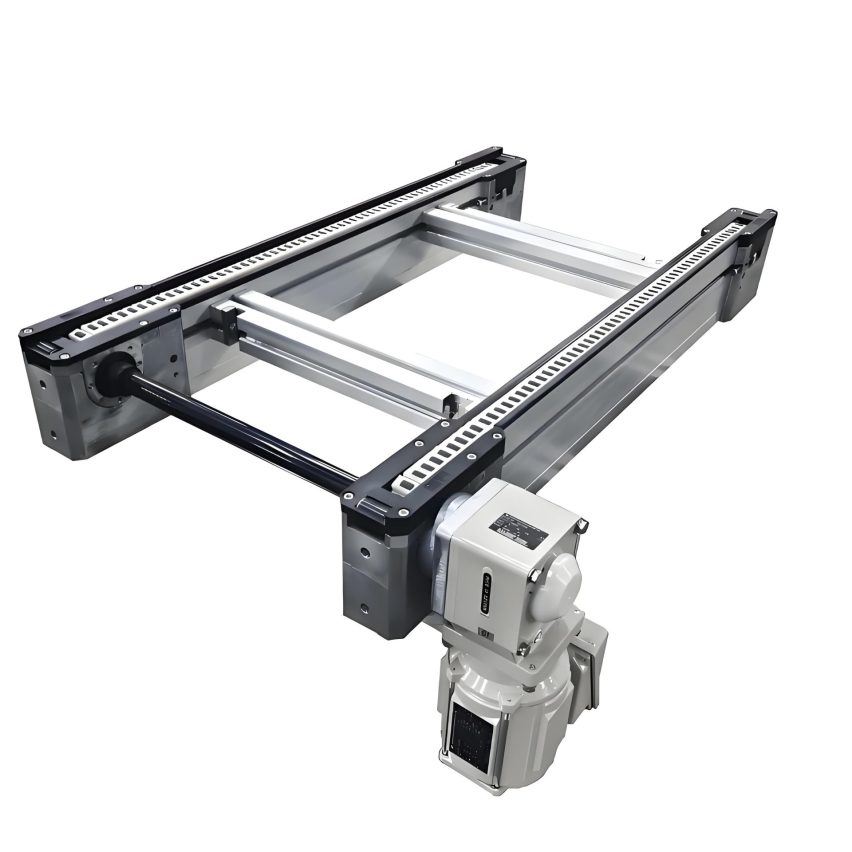
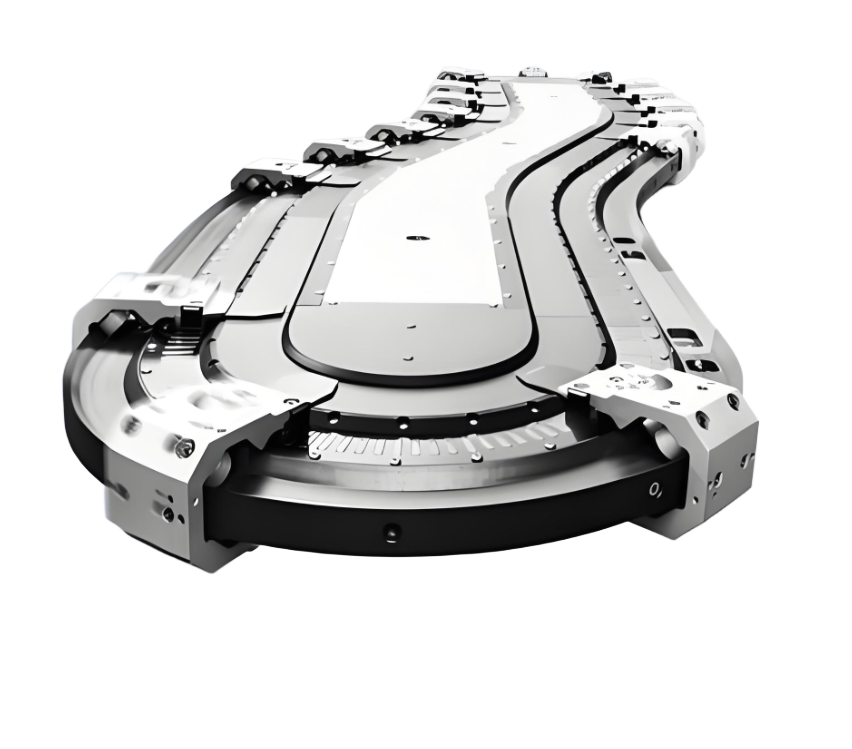
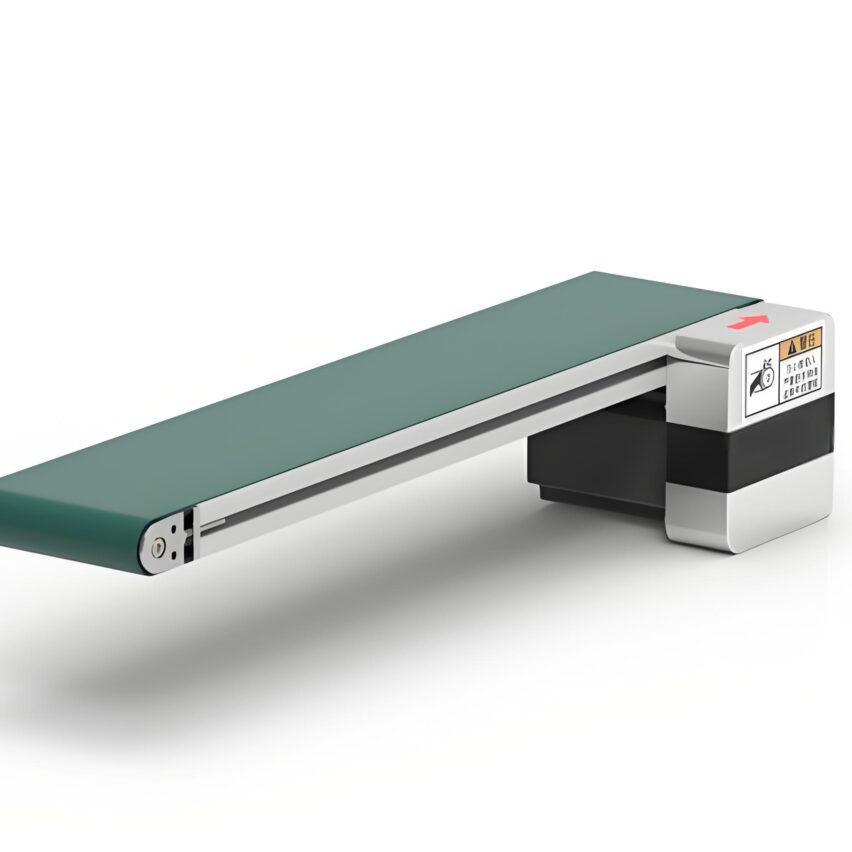
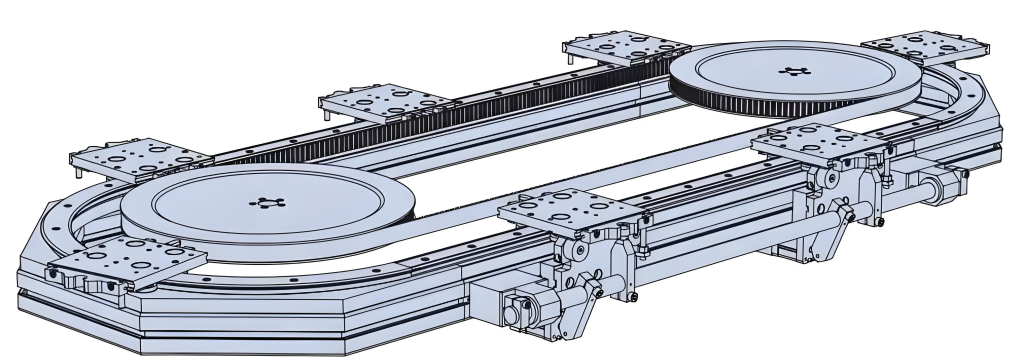
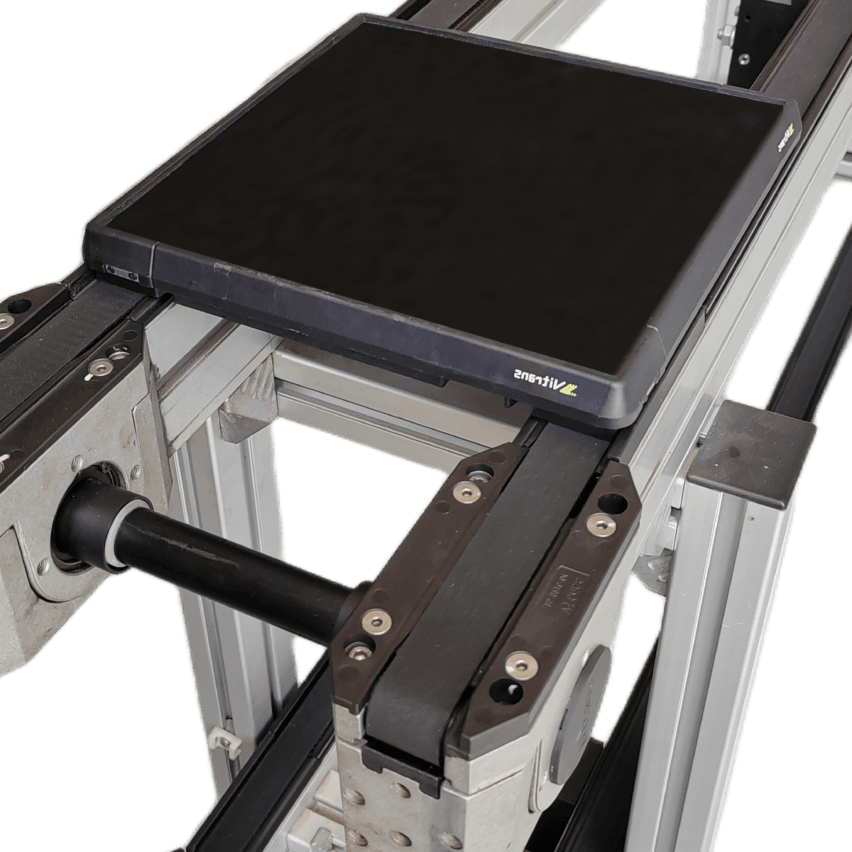
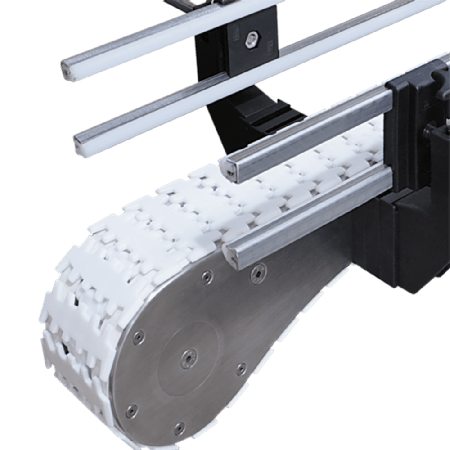
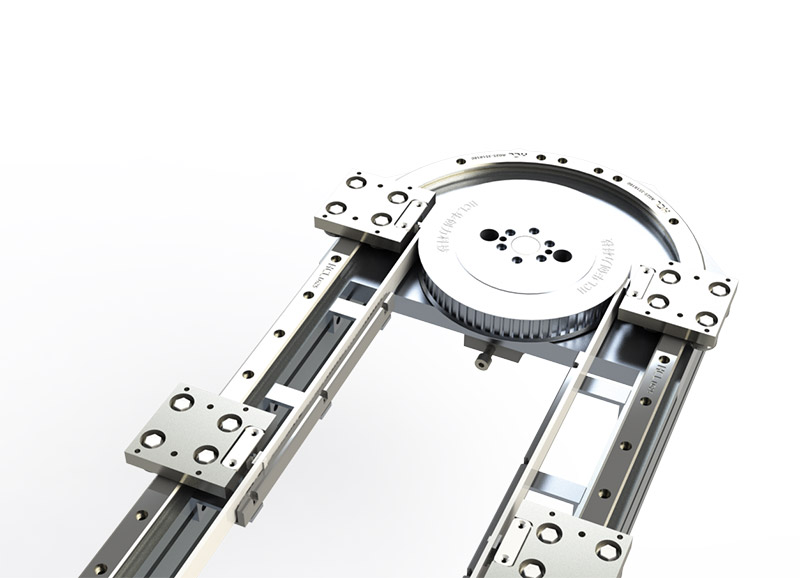
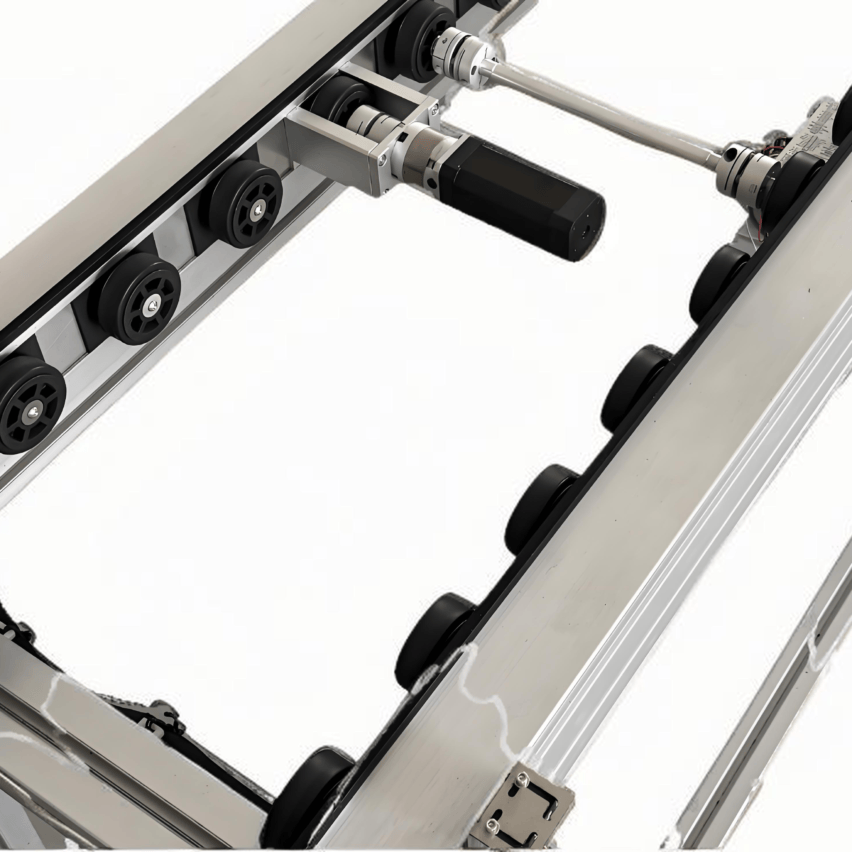
Round belt turning devices play a key role in pallet conveying lines and are mainly used to solve the problem of difficult turning of pallets at right-angle turns due to insufficient friction or pallet structure. Below is a list of its core functions and typical applications:
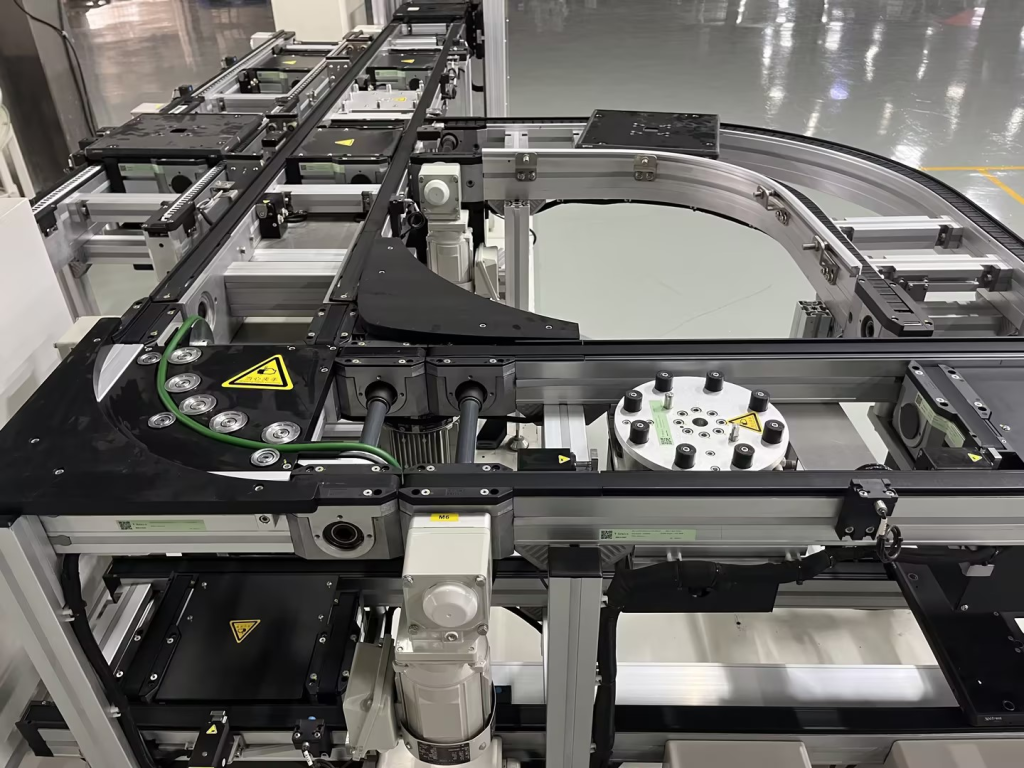

The core of a round belt turncorresponds English -ity, -ism, -ization
In a traditional turn, the pallet relies heavily on the friction between the chain/belt and the bottom of the pallet and the inertia of the pallet itself to complete the steering. However, for:
- Large/heavy pallets: high inertia, high steering resistance
- Pallets with an unstable centre of gravity: prone to tilting or wobbling during turns
- Pallets with low friction on the bottom: e.g. plastic pallets, pallets with high cleanliness requirements or with special coatings on the bottom
- High-speed conveyor lines: higher centrifugal forces, requiring greater control
Friction alone is not enough to push the pallet to complete 90 degrees or 180 degrees of steering steadily and reliably, which can easily lead to skidding, stagnation, jamming, deflection, and even overturning.
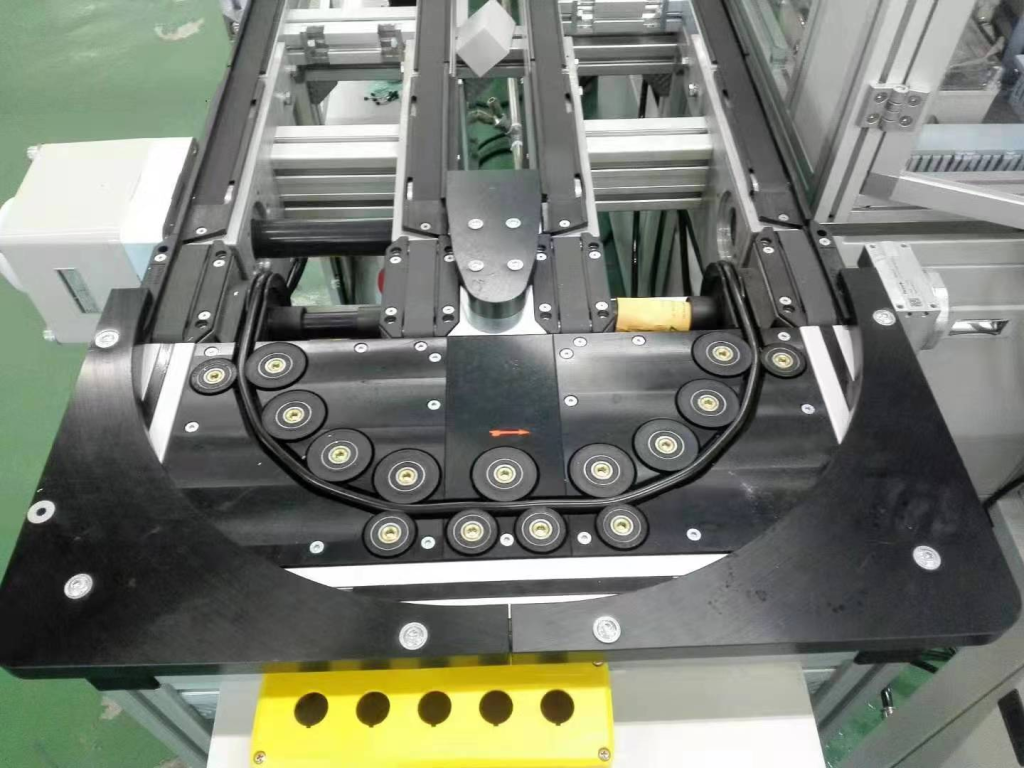

Round belts work.
Installed on the inside of the turn (usually near the inner wall of the inner arc), it provides a constant, strong lateral frictional driving and guiding force by contacting and applying pressure to the sides of the pallet. This acts as a "push" to keep the pallet on the correct turn path, ensuring a smooth, stable and reliable 90 or 180 degree turn.
①Prevent the pallet from running or jamming when turning.
②Improve the reliability and efficiency of the conveyor line.
(iii) Reduced downtime for maintenance by solving the problem of turn jams;
④ Ensure smooth pallet flow and improve the overall system conveying efficiency and throughput;
⑤ Reduce the risk of damage to the pallet (due to jamming, collision or overturning).
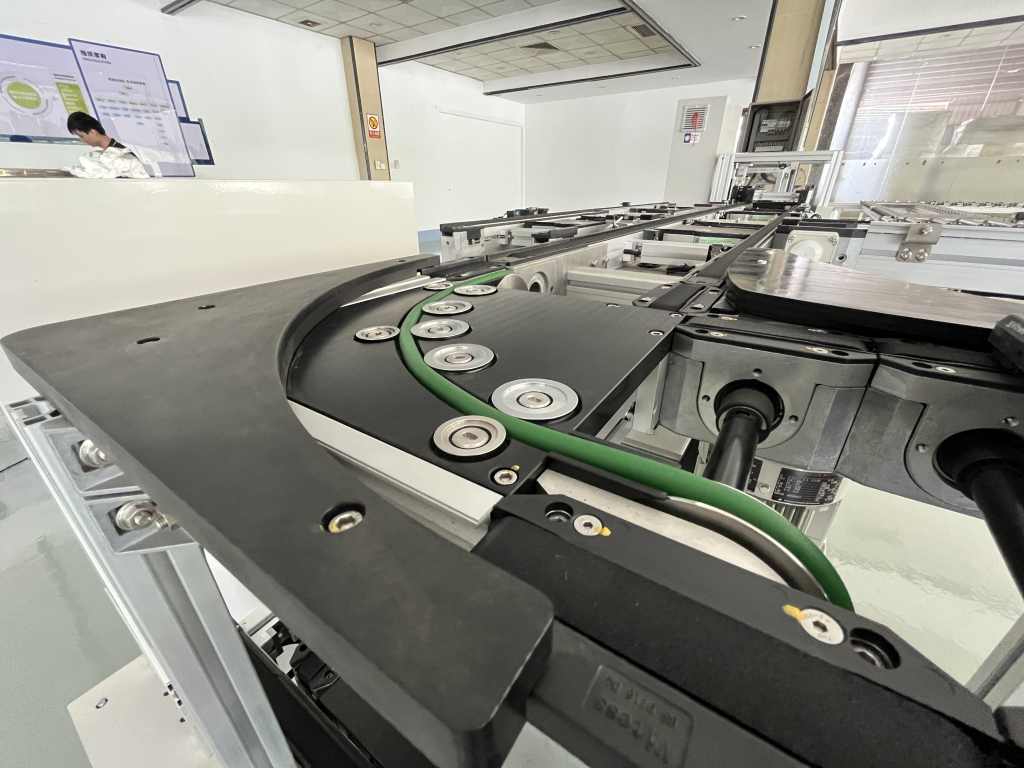

What are the occasions when they are generally used?
90 degree or 180 degree round belt turns are mainly used in scenarios where stability, reliability and efficiency of pallet conveying are required, especially in situations where turning links are prone to problems:
n High-speed pallet conveying and sorting systems
When running at high speed, the centrifugal force of the pallet is large, and conventional turning is very easy to cause the pallet to be thrown out of the track or piled up and jammed, so the round belt turning is a necessary solution to ensure high speed and stable operation.
n Handling of plastic pallets or specially coated pallets
Food and beverage, pharmaceutical and chemical industries often use plastic pallets or pallets with anti-static and anti-corrosion coatings, which have a low coefficient of friction on the bottom surface and are highly susceptible to slippage on roller turns. Round belt turnings act directly on the side and are not affected by the material of the bottom surface.
n Handles heavy or large pallets
manufacturing (e.g., automotive parts, heavy industrial products), and bulk goods warehouses. Heavy pallet steering requires a huge amount of drive force, and the strong side thrust provided by the round belt is the key to reliable turning.
n Where system stability is critical
Airport baggage handling systems (large baggage trays), automated production lines (trays carrying expensive materials), and cold storage (where the coefficient of friction may be lower at low temperatures). In these situations where jams or errors are not tolerated, round belt turns provide a higher guarantee of reliability.
n Layout with compact space and restricted turning radius
Whilst the round belt turn itself does require some space, in some designs it can be more compact than some of the larger chain or jacking rotators, and is suitable where space is restricted but turning must be achieved.
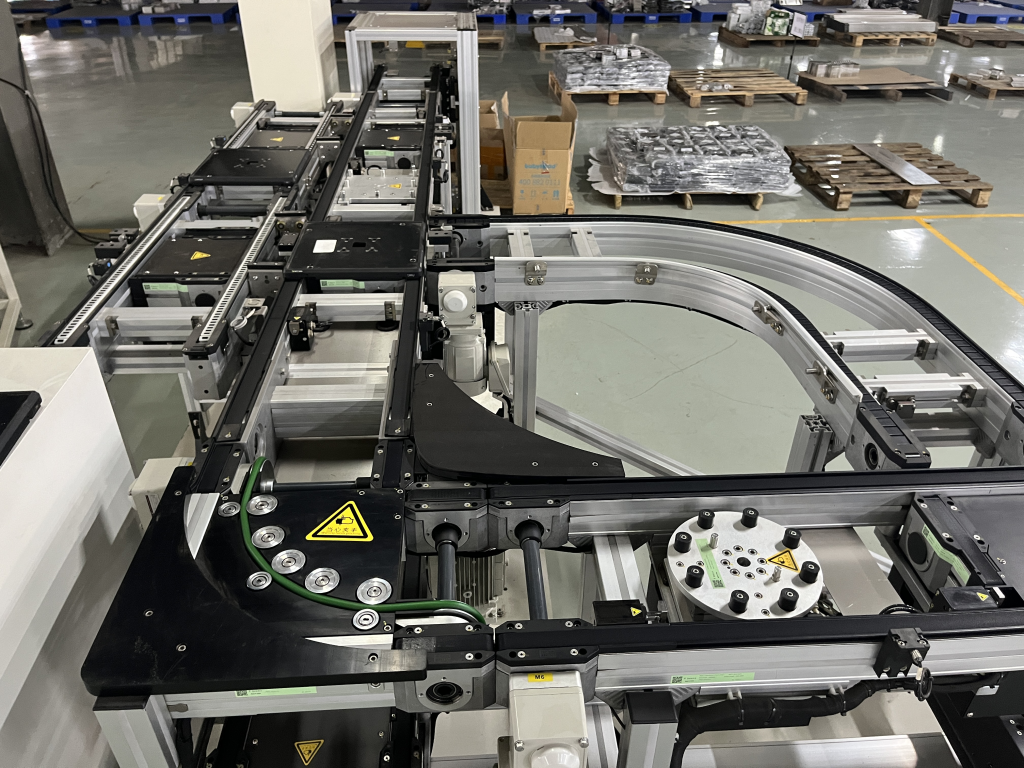

Simply put, when a pallet "won't push" or "will fly" around a corner, round belts are the key technology to make sure it "goes round the corner"!