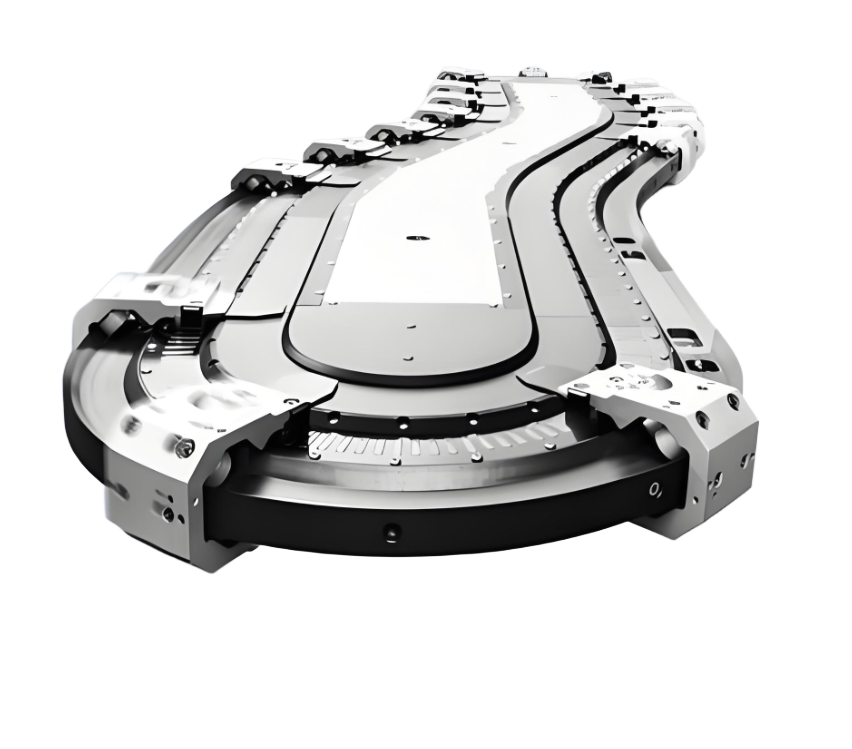
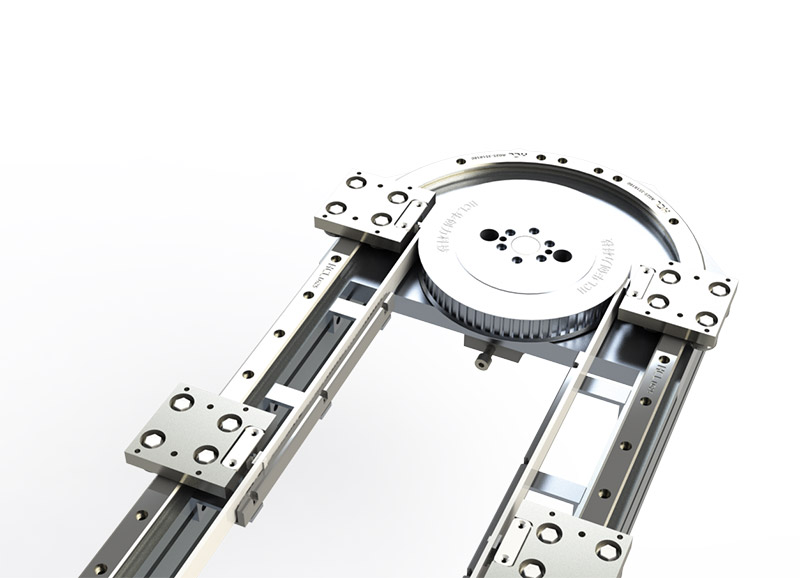
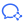
In the field of modern industrial automationSpeed Chain Conveyor LineWith its unique speed increasing mechanism and flexible layout ability, it has become the core equipment to improve production efficiency. Especially in complex production scenarios that require steering, accumulation and multi-station co-operation, its value is more prominent. In this article, we will analyse the technical principles, application scenarios and future development trends of the Speed Chain, as well as incorporate practical insights from the industry.

I. The core mystery of the multiplier chain: structural differences drive growth rates
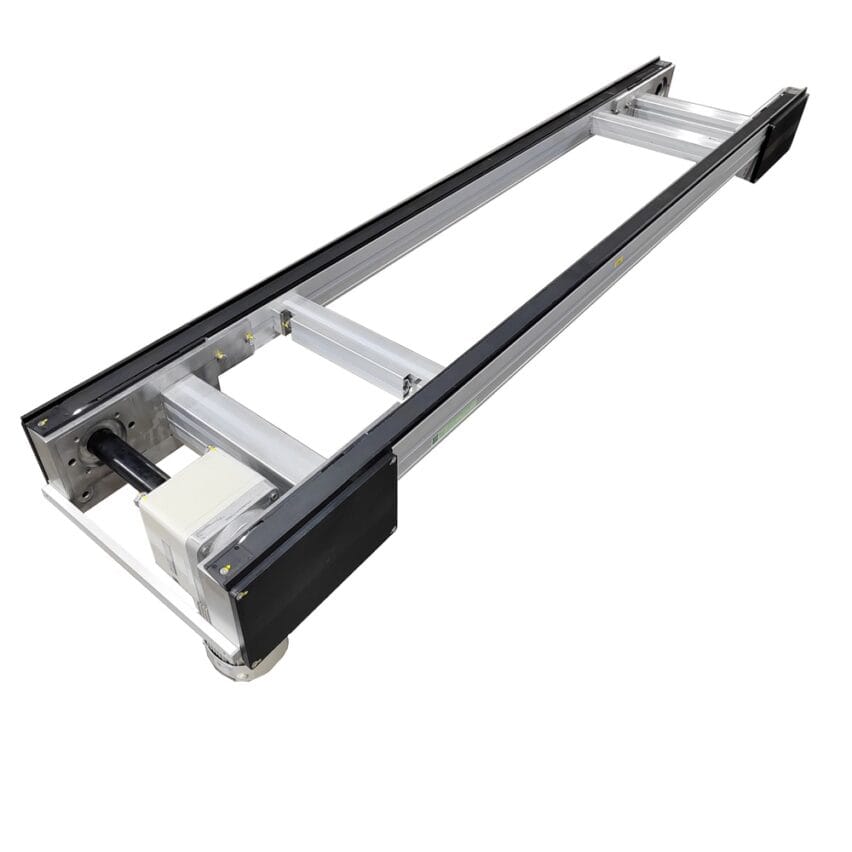
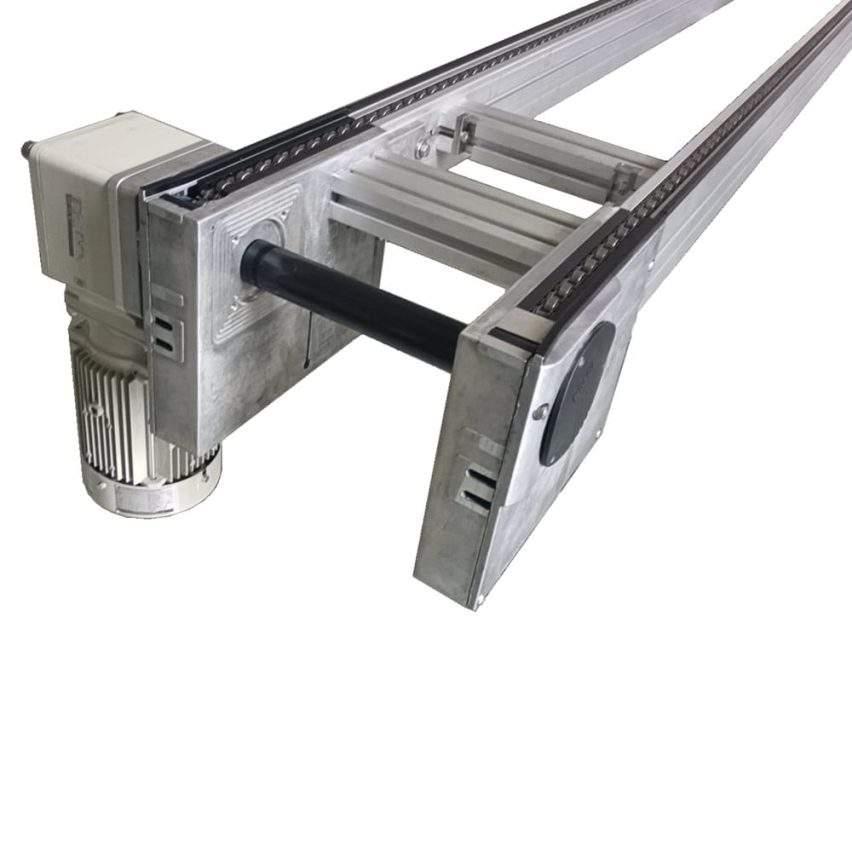
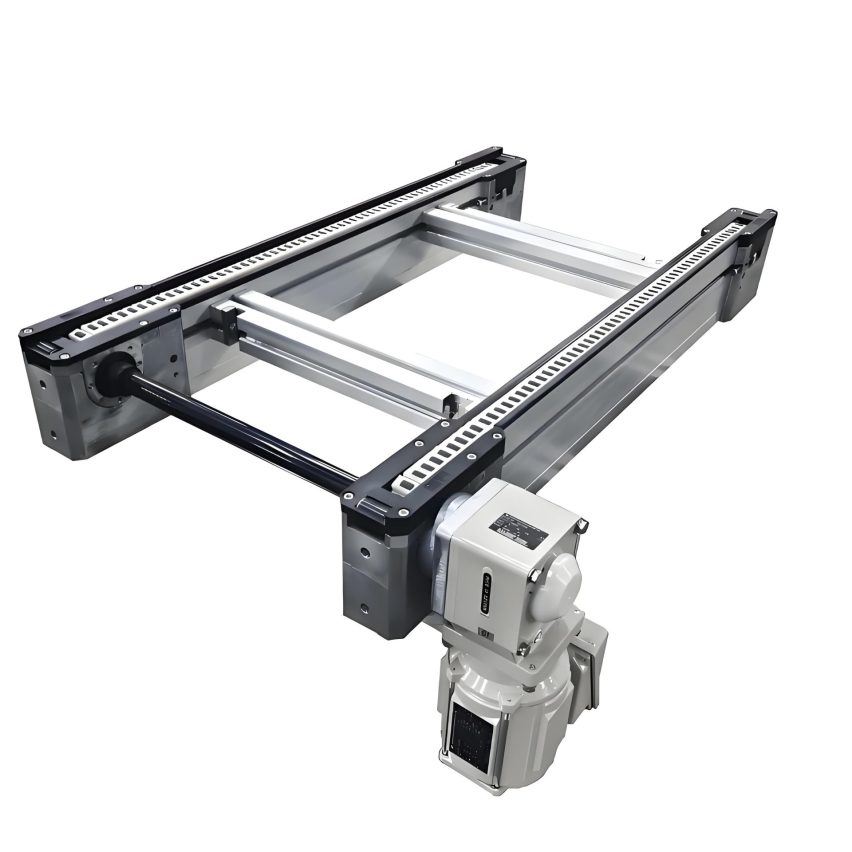
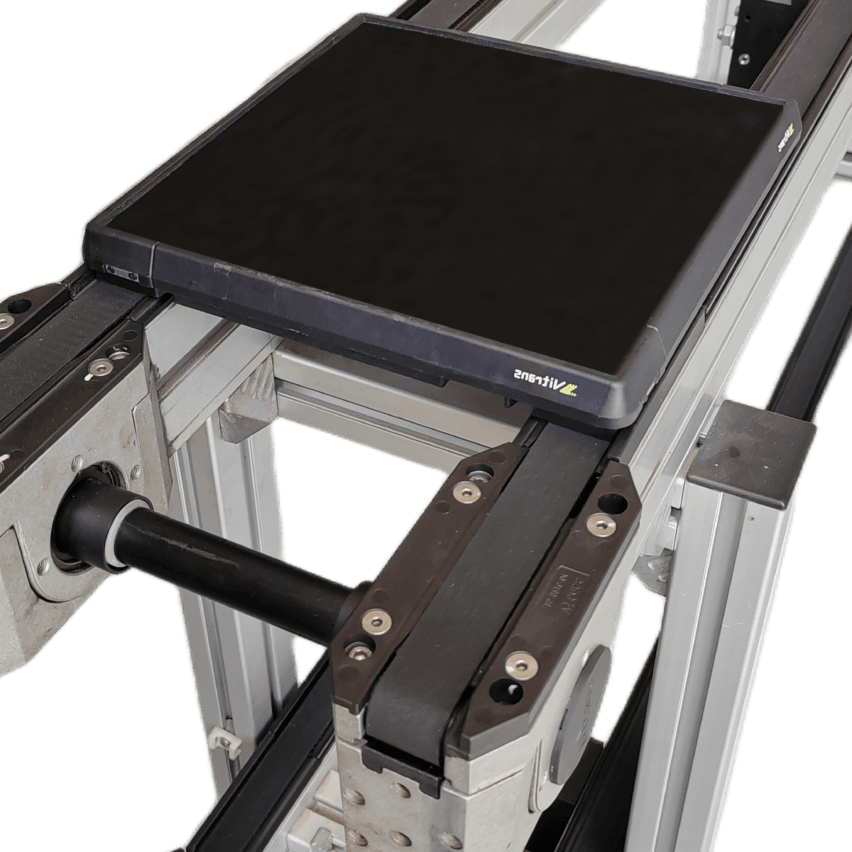
The "speed doubling" effect of the chain is due to its ingenious mechanical design. The chain consists ofTwo sets of key components::
- Internal chain roller(diameter d): contact with the guideway provides the base travelling speed
- External Chain Roller(Diameter D, usually D>d): additional linear velocity due to contact with the tooling plate
According to the principle of motion superposition, the actual velocity of the work plate is given by Eq:
Total V = V₁ × (1 + D/d)
When the roller diameter is twice that of the roller (D=2d), the work plate speed can be up to three times the chain speed. This design allows the machine to operate atLow energy consumption chain driverealiseHigh-speed material handlingThe motor load and wear and tear are significantly reduced.
Second, the engineering advantages of the steering conveyor line
Compared to conventional conveyor lines, speed doubling chains show significant advantages in steering conveyor scenarios:
-
Spatial adaptability
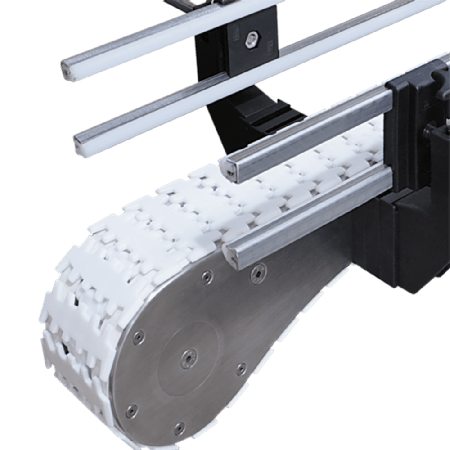
pass (a bill or inspection etc)Circular track designIt realises horizontal steering and supports various layouts such as 90° right-angle turns and S-shaped curves, solving the problem of space limitation in the plant.
case (law): In the electronics factory floor, the Speed Chain compresses the original linear production line by 40% space through a multi-layer steering structure. -
Dynamic beat control
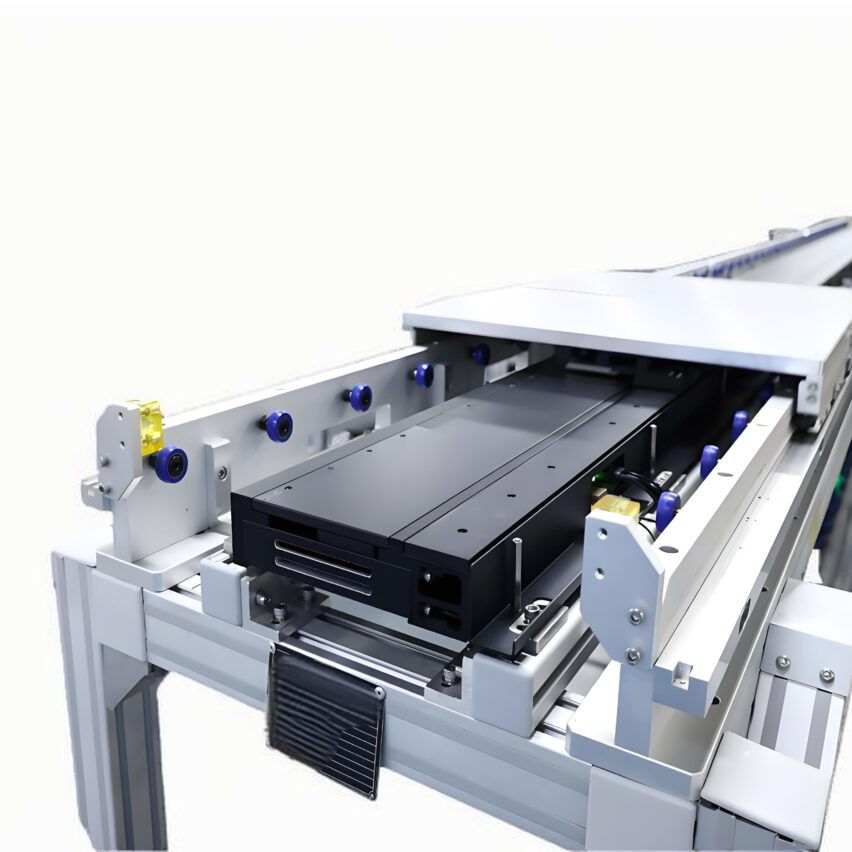
between the tooling plate and the rollersFriction drive mechanismThe chain is designed to be used as a stopper, allowing the stopper to pause at any time for localised stations of material while the chain continues to run. Realisation:- Adjustment of hours of independent work at each station
- Faulty workstation isolation does not affect the whole line
- Precise positioning (±0.05mm) for robot gripping
-
Super load compatibility

Roller type carrying capacity Applicable Scenarios Engineering Plastic Roller ≤2000kg 3C electronics, light assembly Steel Roller ≤4000kg Engine, Battery Pack
Third, the industry application scene breakthrough
- automobile manufacturing: On the steering conveyor line, the doubling chain carries the engine block through thejack-up transplanterRealisation of 90° turn line between assembly and inspection stations, reducing the beat to 45 seconds/unit.
- 3C electronics: Mobile phone assembly line usingMulti-layer multiplier chain reflux systemThe system integrates visual inspection at the steering node, and faulty products are automatically diverted to the repair lane.
- new energy: In photovoltaic cell transport.Ceramic coated rollersAvoid scratching the silicon wafers, and control the speed difference at the turn within 5%.
IV. Key Design Challenges and Solutions
-
Misconceptions in the selection of multiplier ratios
Theoretical 3x speed in practice only up to 2.7x (due to friction losses). Recommendation:- 2.5x speed chain for light load environment (2.3x measured)
- Heavy-duty, high-speed option with 3x speed chain (2.7x measured)
-
Steering Section Slip Prevention and Control
Countermeasures against the tendency for the work plate to deflect at small turning radii include:
- riseGuide rails
- adoptionDifferential sprocket setCompensation of speed difference between inner and outer ring
- Roller surface additionPolyurethane anti-slip pattern
Principles of Line Segmentation
Length of single section ≤ 12m(Over-length will easily cause the chain to run out of direction), if exceeded, need to be driven in sections and reservethermal expansion gap.
V. Future development trends
- intelligent fusion
IIoT sensors are embedded in the rails to monitor chain tension and roller temperature in real time, and predictive maintenance reduces downtime by 70%. - Material innovation
Carbon fibre composite rollers were tested to be 50% lighter and 3 times more resistant to abrasion, making them particularly suitable for cleanroom environments. - The Modular Revolution
Introduced the "Lego" steering module, which supports rapid reorganisation of the production line layout in the field, compressing the changeover time from 2 weeks to 48 hours.
Self-questioning: the core issue of speed chain steering conveyor lines
Q1: Why is the work plate not easy to come off when turning?
A: The steering track usesTilting angle designThe centrifugal force is transformed into the guide wheel adherence force (usually 3°-5° inward tilt); at the same time, the bottom of the work plate is equipped with an additionalAnti-tipping flange, double guaranteed stability.Q2: How to balance the contradiction between growth rate and accuracy?
A: AdoptionThree-stage control strategy: Acceleration in linear section → deceleration before steering → creep feed in positioning section to achieve ±0.1mm positioning in a 30m long line body.Q3: Why not just increase the chain speed instead of the doubling structure?
A: High speed operation of the chain can causeresonance noise(up to 85dB at 15m/min over) andwear and tearThe double-speed design achieves a high speed of 30m/min for the tooling plate while maintaining a chain speed of <10m/min.
The value of the speed chain steering system goes far beyond the conveyor itself - it is reconfiguring the logic of the production space. When the traditional assembly line is replaced by a spatially folded three-dimensional conveyor network, the boundaries of the factory will expand once again.