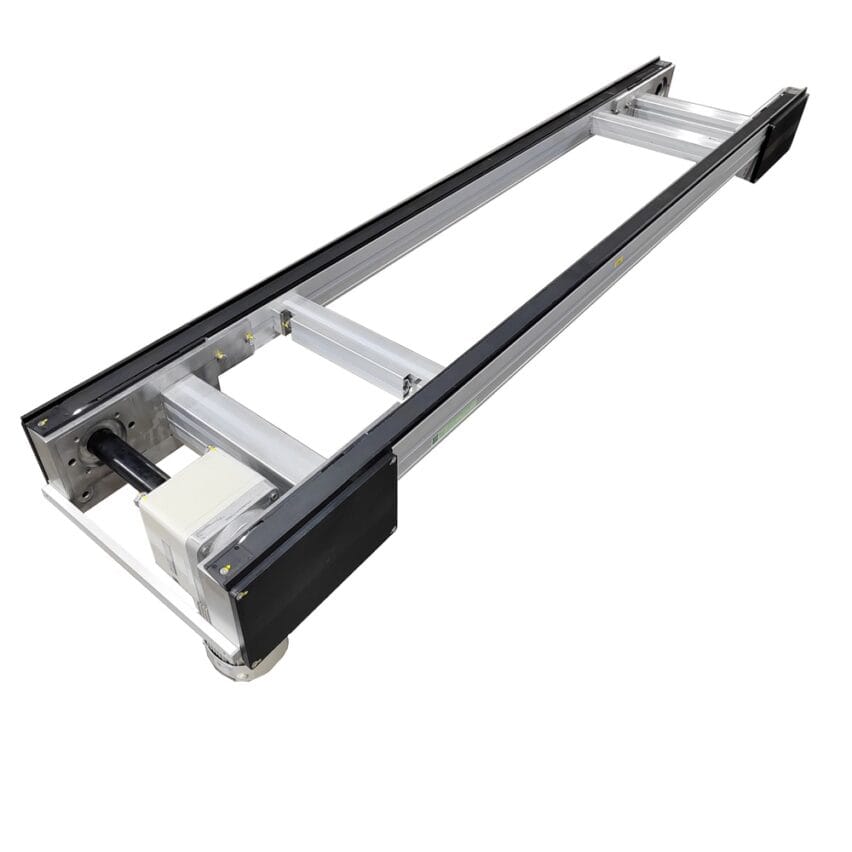
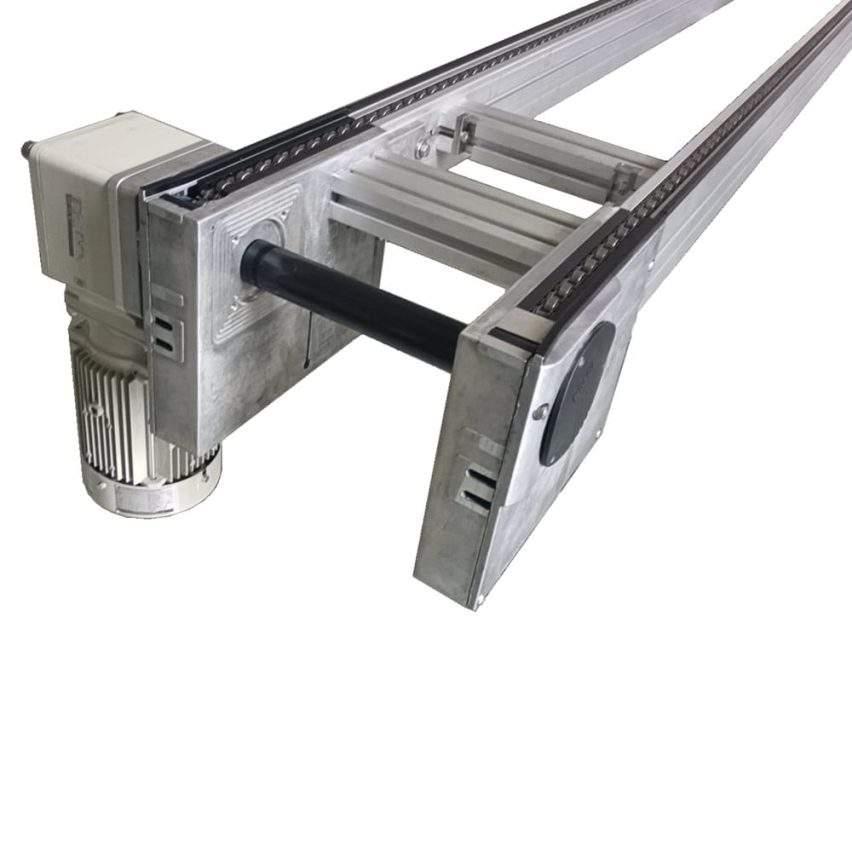
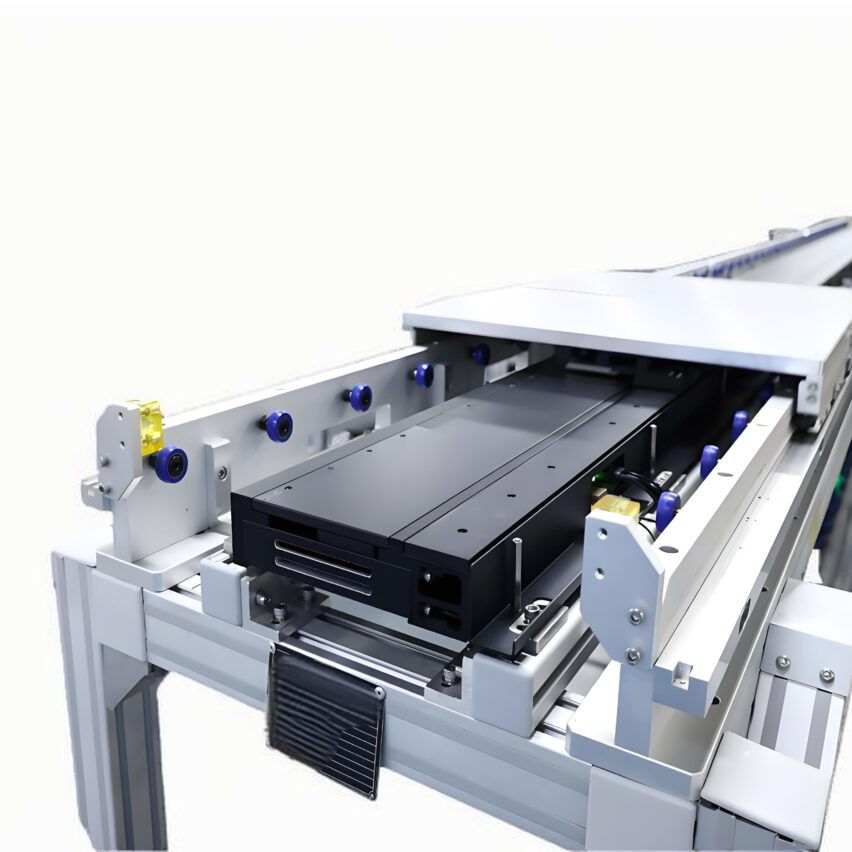
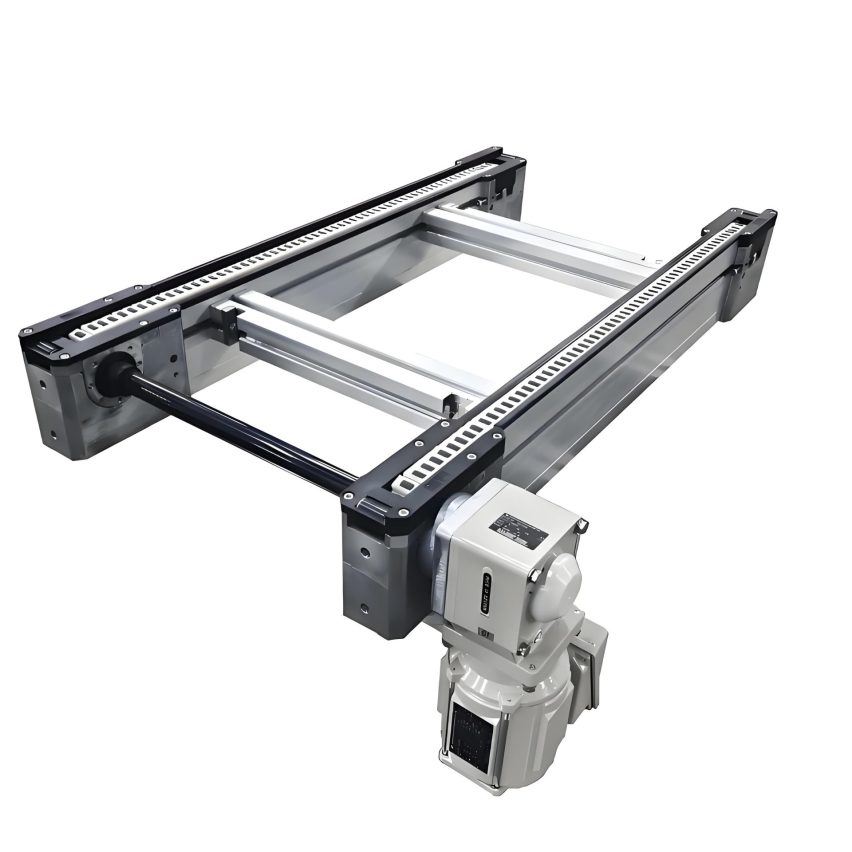
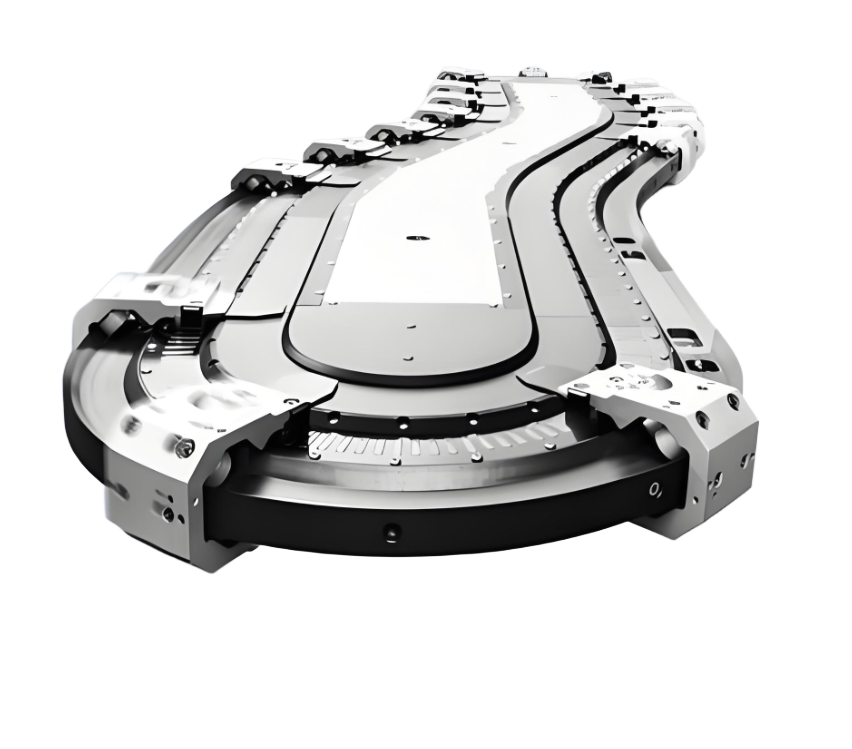
### A breakthrough in the core principle and miniaturisation of the multiplier chain
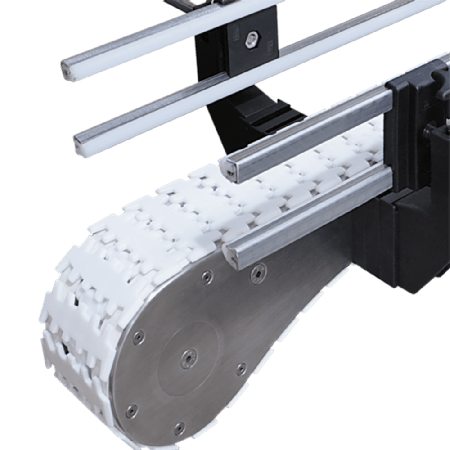
The multiplier chain (differential chain) is designed by means of a uniqueMechanical differential designEfficient conveying: When the chain is running, the pallet carrying the workpiece moves at only 1/2.5 to 1/3 of the actual speed of the chain, and this "fast-chain-slow-plate" feature allows the workpiece to be accurately paused at the workstation during the conveying process without having to stop the entire production line. For example, in the electronics assembly scenario, the triple-speed chain conveys at a high speed of 20 metres/minute, but the actual speed of the workpiece plate is only about 6.7 metres/minute, leaving plenty of time for workers to operate.

The innovations of the miniaturised design areBalancing space and efficiency::
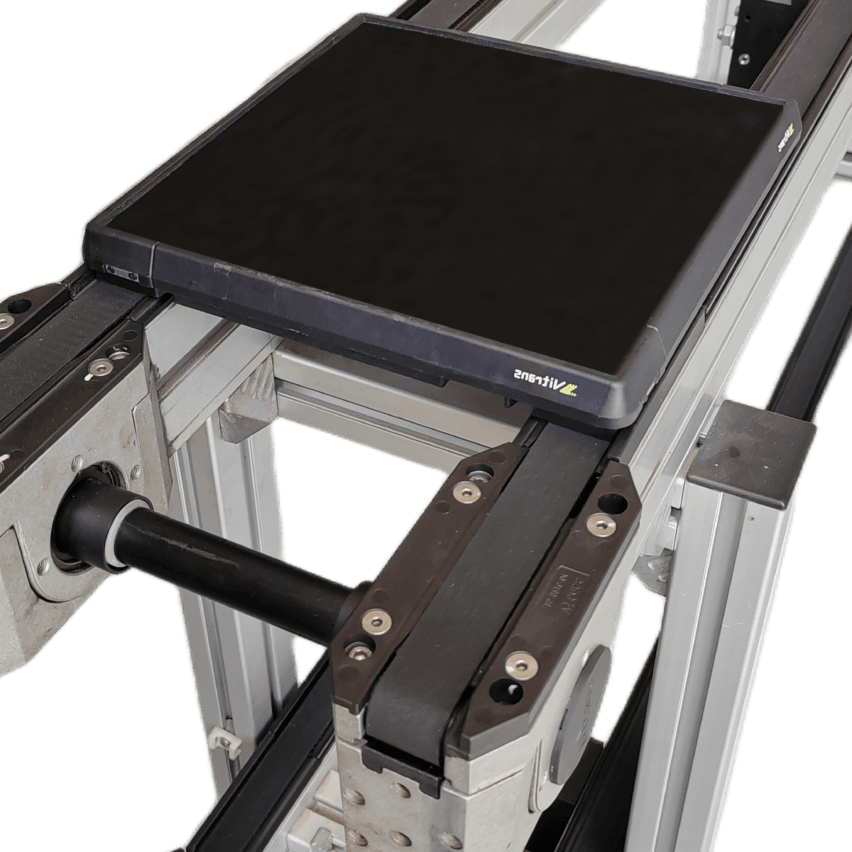
- Compact Drive SystemsAdopting 0.75-2.2kW gear motor, supporting single section 10-15m line body (traditional production line needs more than 40m), reducing 30% footprint.
- Lightweight construction: Aluminium profile guide (40 * 80mm) instead of steel frame, weight reduction of 50% still maintains ≤0.5mm/m linear accuracy.
- accumulation conveyor: Independent start/stop of workstations through cylinder blockers (response time ≤ 0.5 seconds), eliminating wasteful waiting between processes.
Innovative practices for space optimisation design
Against the backdrop of soaring land costs, the layout of production lines for small factories needs to think outside the box:
#####Ring closure design
Connecting the first and last straight line sections into a closed loop, typical application cases show that: in 80 square metres of workshop, the ring layout reduces the footprint by 40% compared to the straight line type, and at the same time, through theDouble Reflux System(Upper conveyor, lower empty board return) Enhance vertical space utilisation.
#####Dynamic workstation planning
- Workstation spacing compressed to 1-1.5 metres (conventional lines require more than 2 metres)
- Liftable table with carbon fibre tooling plate (5kg deadweight/100kg load) to achieveErgonomic Adaptation
- Modular expansion interface, reserved AGV docking channel to support future unmanned upgrade
personal viewpoint: The current bottleneck in small multiplier chains is the ability to flexibly change production. We have found in our automotive electronics projects that byMagnetic Quick-Change Clamps(non-standard parts clamping time reduced from 45 minutes to 3 minutes) can significantly increase the versatility of the production line, which will be the competitive focus of the next generation of technology.
Modular design for flexible production
In response to the trend towards high variety and small batch sizes, the miniature multiplier chain is flexibly adapted through the reorganisation of the three main modules:
#####1. Reconfigurable transport units
- Standardised 2m/4m/6m track sections, splicing accuracy ≤ 0.5mm
- Mixed use of two-speed chain (2.5 times speed) and three-speed chain (3 times speed) according to process requirements: steel rollers for heavy-duty stations and engineering plastic chains for light-duty stations to reduce noise.
#####2. Smart pallet systems
| typology | Applicable Scenarios | Technical Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| baseboard | Assembly of light appliances | Cost Reduction 40% |
| Engineering Plastic Sheet | Anti-static requirement area | Integrated RFID chip to trace production data |
| Composite steel plate | Engine component assembly | High temperature resistance of 350°C, positioning accuracy ±0.1mm |
#####3. Quick-change mechanism
Pneumatic lifting transplanter (500kg load) for material transfer between lines.Changeover time compressed from 2 hours to 15 minutesThe switching efficiency is 87% higher than that of the traditional production line.
Technology upgrades for intelligent control systems
The "nerve centre" of the mini-multiplier chain is undergoing a triple transformation:
Distributed Control Architecture
Each station is equipped with an independent PLC sub-station (e.g. Siemens ET200SP), which is connected to the main controller via the EtherCAT bus, reducing the troubleshooting time from an average of 30 minutes to 45 seconds.
Dynamic Beat Adjustment Algorithm
Capacity prediction system based on machine learning, real-time adjustment of chain speed (0.5-5m/s stepless variable speed). Actual operation data shows that this technology has increased the average daily capacity of small battery pack production line by 22%.
Preventive maintenance mechanisms
Vibration sensor (sampling rate 10kHz) + current monitoring module, early warning of chain wear or motor abnormality. After the application of a medical device factory, the rate of sudden equipment failure decreased by 68%.
Implementation Path and Industry Adaptation Strategy
#####Phased deployment routes
- Prioritise the conversion of bottleneck workstations(e.g. tightening/testing stations)
- Addition of servo positioning module (repeatability 0.05mm)
- Integrated 3D Vision Sensor (Keens IV3 Series)
- Base line laying
- Choose 2.5x speed chain for loads up to 30kg.
- Configuration of 220V power supply system to reduce the cost of retrofitting
- Intelligent Expansion
- Access to MES system via 5G edge gateway
- Addition of collaborative robotics workstations
#####Customised solutions for the industry

- electronics industry: Anti-static chain + Class 1000 cleanliness design
- Automotive parts and components: High-temperature resistant nickel-plated chain (150°C continuous operation)
- medical equipment: Stainless steel + IP54 protection
Cost-effectiveness data: The case of small home power plants shows thatInitial payback cycle can be reduced to 1.5-2.5 years(3-5 years for traditional production lines), OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) increased from 65% to 92%.
Future Development Trends and Technology Outlook
Digital Twins Drive the Design Revolution
Through FactoryIO and other platforms to build virtual models of production lines, the simulation error rate is controlled within 5%, reducing the cost of trial and error by more than 60%. A motor assembly project proved that virtual debugging compressed the production cycle from 8 weeks to 11 days.
Hybrid delivery mode
The combination of speed chains and magnetic levitation technology is being tested: contactless levitation transmission is used at the inspection station, eliminating the impact of mechanical vibration on precision measurements and increasing the yield rate by 1.7 percentage points.
Green energy-saving innovations
The new regenerative braking system recovers the energy from the falling position of the workpiece, and the experimental data shows that the power saving rate reaches 18%. Together with the AI energy management module, the power output curve of the motor can be further optimised.
Self-questioning: understanding the core issues of small multiplier chains
Q1: What is the essential difference between a speed multiplier chain and a traditional belt line?
centreDifferential mechanism and accumulation function. The speed doubler chain achieves separation of chain and pallet speeds through the roller-roller radius difference, allowing workpieces to be stopped independently; whereas the belt line must be started and stopped in full, resulting in lost capacity.
Q2: What are the most important performance parameters for small plants to focus on?
Key Four:
- position accuracy(within ±0.5mm, dependent on pneumatic stopper)
- Maximum load(Aluminium profile structure recommended ≤100kg/station)
- environmental adaptation(Temperature and humidity fluctuations require special chains)
- Extended Redundancy(20% electrical interface reserved)
Q3: How to maximise space utilisation?
adoptionCircular Layout + Vertical Return DesignTypical examples are shown in a 150 m² plant:
- Linear layout: accommodates 4 stations
- ring-optimised version: 6 stations + central material area.Space utilisation upgraded by more than 40%
Q4: Core technical support for flexible production?
Modular tooling systemIt's the core:
- Magnetic fixture enables 15-minute changeover
- RFID Pallet Auto-ID Product Specifications
- Motorised width adjustment mechanism for multi-sized workpieces
Q5: Why do control systems favour edge computing architectures?
To reduce response latency:
- Photoelectric sensor signals are processed at the local PLC sub-station (<10ms)
- Only critical data uploaded to the cloud, reducing bandwidth requirements by 75%
- Basic production can be maintained in case of disconnection
Q6: How are maintenance costs controlled?
realiseOn-demand lubrication strategy::
- Traditional: Fixed 30-day cycle maintenance
- Intelligent: vibration sensors monitor chain wear, dynamically triggering maintenance
An enterprise's annual maintenance costs have fallen by 411 TP3T as a result.