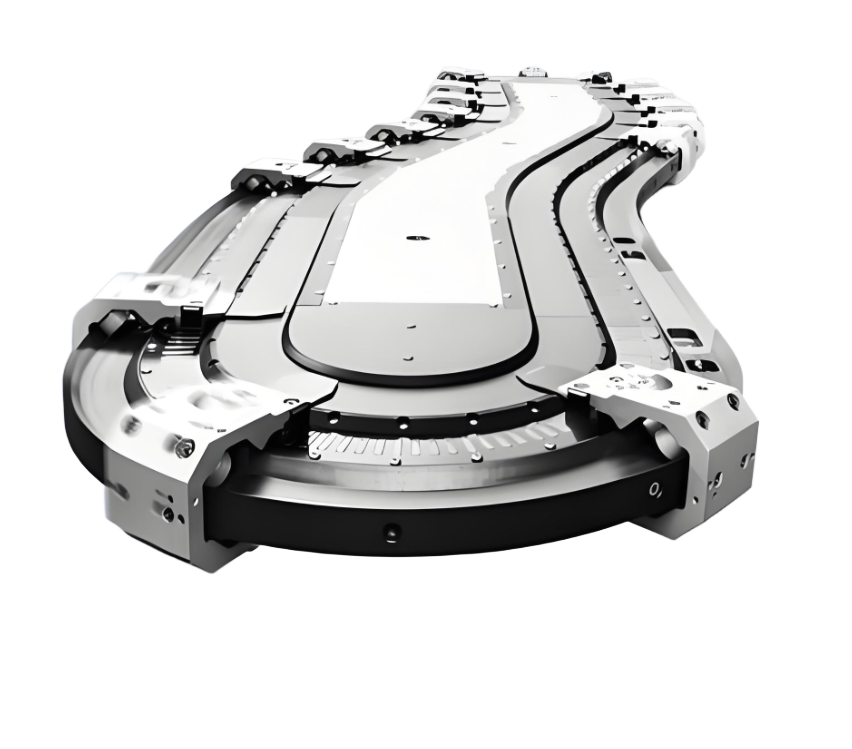
Pain point analysis: why traditional conveyor lines are inefficient at right-angle turns?
Battery production workshops commonly use rectangular layouts to save space, but straight conveyor lines cannot accommodate right-angle steering requirements. There are three major drawbacks to traditional solutions:
- Robot gripping steering: Small number of single handlings (usually 1-2), long beat times and high docking accuracy requirements;
- circular orbit steering: The bending radius needs to be ≥1.5 metres, the occupied area increases by 40%, and it is easy to cause the battery to shift due to centrifugal force;
- Lifting Roller Auxiliary: Need to reserve equipment rotation clearance to extend battery waiting time 20% or more.
Core technology innovation: How to achieve seamless right-angle steering in compact spaces?
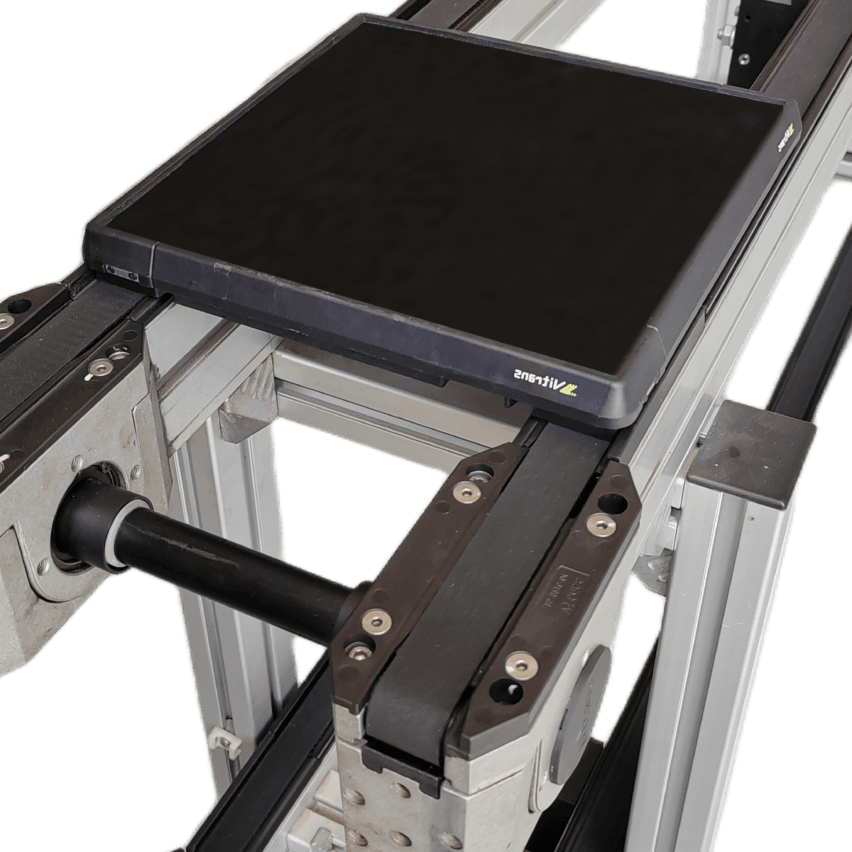
Hydraulic universal angle adjustment technologyBecoming the key to break the ice, its design contains two core modules:
-
Four-corner linkage hydraulic system
- The bottom of the support plate is equipped with 4 groups of independent hydraulic telescopic mechanism, connected by universal joints (including movable ball and hollow column structure);
- The support plate is tilted by 15° by contracting diagonal hydraulic cylinders (e.g. the second and fourth cylinders), using gravity to guide the battery to slide into the steering area;
- After reset, another pair of angle hydraulic cylinders is activated to achieve 90° direction switching, the whole process takes ≤3 seconds.
-
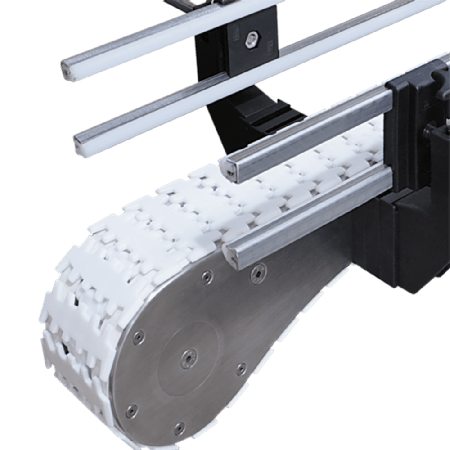
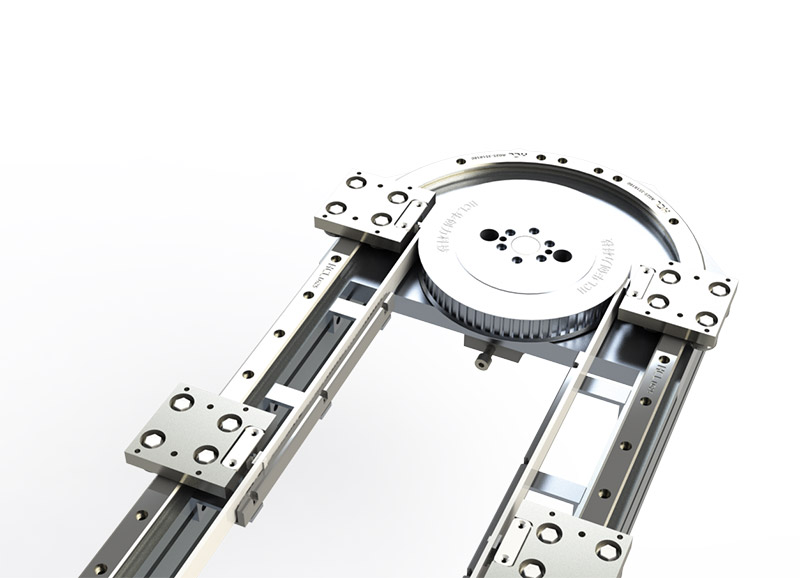
Eccentric rotating mechanism
- The frame rotates around the eccentric shaft under the action of the drive motor from the first position (docking upstream) to the second position (docking downstream);
- Conveyor belts are synchronised for orientation, avoiding interference with upstream and downstream equipment and reducing the 1.2 m buffer spacing required by conventional solutions.
Compare and contrast with traditional programmes:
norm Hydraulic universal adjustment Robot Grabbing circular orbit (in astronomy and in astronautics) turn time ≤3 seconds ≥8 seconds progression space requirement 0 added +30% +40% position accuracy ±0.5mm ±1mm ±2mm
Anti-jamming key technology: how to solve the offset and pile-up during steering?
Three-tier anti-skew mechanismIt is the core of guaranteeing smooth operation:
- Level 1 infrared real-time monitoring
The conveying line is fitted with opposing infrared sensors on both sides of the line, and the system triggers a corrective command within 0.1 seconds when the cell offset touches the optical path; - Dynamic adjustment of secondary push plates
The linear module drives the L-type push plate to move laterally, together with the roller-type limit structure to push the battery back to the centre line, with a stroke control accuracy of ±0.3mm; - Forced correction of three-stage guide wheels
Nylon covered guide wheels (15cm OD) are installed in the steering area to cushion the collision force through the protective layer and to guide the battery to its home position with a tilting design.
Intelligent Sorting Buffer SystemResponding to high-traffic scenarios:
- Blocking mechanism linkage: The baffle drops to intercept subsequent batteries, freeing up operating space in the steering area;
- Bulkhead Group Positioning: Once the battery enters the steering area, a multi-panel divider separates it into separate cells to avoid collisions during steering;
- RFID Priority Scheduling: Automatic identification of battery batches, priority steering for urgent tasks, and reduction of production line waiting rates.
Industry outlook: which scenarios are best suited for the technology?
Differences between lithium and lead-acid battery scenarios::
- Lithium Battery Pack: Due to the small size (usually ≤20cm) and light weight of the cells, it is suitable for multi-channel parallel steering design (e.g. 4 cells/group), and synchronised steering is achieved through the spacer limiting section;
- lead-acid battery: If the weight of single unit is more than 15kg, it is necessary to strengthen the support structure (e.g. increase the pulley frame to assist the rotating plate load-bearing) and configure the dual motor drive to prevent overloading.
50% cost-effectiveness improvement over conventional programme::
- Taking the workshop with an annual production capacity of 1 million batteries as an example, the right-angle steering system reduces the equipment footprint by 200 m², which is equivalent to saving 180,000 RMB/year in rent;
- The jam failure rate was reduced from 12 times/day in the traditional solution to ≤ 1 time/week, reducing maintenance costs by 35%.
The future lies in modular expansion: through standardised universal joint interfaces, it supports the rapid retrofitting of inspection modules (e.g. electrode contact self-inspection devices) and the integration of steering and quality control processes. The right-angle turning conveyor line is not only a space optimisation tool, but also a pivotal node for intelligent manufacturing process re-engineering.